1 Name of Medicine
Ramipril.
2 Qualitative and Quantitative Composition
Each tablet contains 2.5 mg, 5 mg or 10 mg ramipril as the active ingredient.
For the full list of excipients see Section 6.1 List of Excipients.
3 Pharmaceutical Form
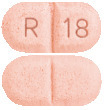
APO-Ramipril Tablets. 2.5 mg tablet. Pink to red mottled, oblong tablet with R and 18 on either side of score line on one side and score line on the other side.
5 mg tablet. Light yellow to yellow mottled, oblong tablet with R and 19 on either side of score line on one side and score line on the other side.
10 mg tablet. Light yellow to yellow mottled, oblong tablet with R and 10 on either side of score line on one side and score line on the other side.
4 Clinical Particulars
4.9 Overdose
In cases of overdose, the following may occur: excessive peripheral vasodilation, severe hypotension, shock, bradycardia, electrolyte disturbances, renal failure.
The treatment given depends on how and when the drug was taken and on the type and severity of symptoms. Steps must be taken to eliminate ramipril which has not yet been absorbed (e.g. administration of adsorbents during the first 30 minutes if possible). Vital and organ functions must be monitored under intensive care conditions and safeguarded if necessary. In case of hypotension, administration of α1-adrenergic agonists should be considered in addition to volume and salt substitution.
No experience is available concerning the efficacy of forced diuresis, altering urine pH, haemofiltration or dialysis in speeding up the elimination of ramipril or ramiprilat. If dialysis or haemofiltration is considered, consideration must be given to the fact that ramipril is contraindicated with certain high flux filtration membranes and with dextran sulfate LDL apheresis (see Section 4.3 Contraindications).
For information on the management of overdose, contact the Poisons Information Centre on 131126 (Australia).
5 Pharmacological Properties
5.3 Preclinical Safety Data
Genotoxicity. No data available.
Carcinogenicity. No evidence of a carcinogenic effect was found when ramipril was given to rats (up to 500 mg/kg/day for 24 months) or to mice (up to 1000 mg/kg/day for 18 months).
An increased incidence of oxyphilic cells in the renal tubules and oxyphilic microadenomas was observed in rats treated for 24 months with ramipril (3.2 - 500 mg/kg/day). Data from historical control animals showed that the spontaneous occurrence of oxyphilic cells in rat kidney is age-related, is higher in males and reaches a level similar to that seen in the ramipril treated group. There is no evidence in humans that the occurrence of oxyphilic cells is age-related. Moreover, progression of oxyphilic cells to neoplasia (oncocytoma) is rare and, when it occurs, is considered to be benign. Whether this finding in rats represents any potential risk to man is therefore unclear.
Fibromuscular pad formation. In several repeated dose studies in rats, especially male animals treated with ramipril (3.2 - 500 mg/kg b.w./day) showed an increased incidence of so-called fibromuscular pad formation in the basal region of the gastric mucosa. The findings suggest an increased connective tissue formation and partly also increased formation of smooth muscle (lamina muscularis mucosae) due to a predominantly round cell inflammatory reaction. In all studies (1 - 24 months, carcinogenicity) the changes are always of the same type and no tendency of proliferation is obvious. Thus, it seems to be rather a reactive process with circumscribed scar tissue formation. The changes in the rat stomach mucosa could not be reproduced in other species (i.e. mouse, dog, rabbit, monkey).
This lesion was also observed when rats were treated with a relatively high dose (90 mg/kg/day for 3 - 6 months) of another ACE inhibitor. In the light of the available data, fibromuscular pad formation in the rat would not appear to present a serious risk in humans.
6 Pharmaceutical Particulars
6.7 Physicochemical Properties
Ramipril is a 2-aza-bicyclo [3.3.0]-octane-3-carboxylic acid derivative. It is a white or almost white, crystalline powder sparingly soluble in water, freely soluble in methanol. Ramipril melts between 105°C and 112°C.
Chemical structure.
https://stagingapi.mims.com/au/public/v2/images/fullchemgif/CSRAMIPR.gif Ramipril has 5 chiral centres, with S-configuration in all 5 asymmetric carbon atoms.
Chemical name: (2S,3aS,6aS)-1-{N-[(1S)-1-(ethoxycarbonyl)-3-phenylpropyl]-L-alanyl} octahydrocyclopenta[b]pyrrole-2-carboxylic acid.
Molecular formula: C23H32N2O5.
Molecular weight: 416.51.
CAS number. 87333-19-5.
7 Medicine Schedule (Poisons Standard)
S4 - Prescription Only Medicine.
Summary Table of Changes
https://stagingapi.mims.com/au/public/v2/images/fulltablegif/APRAMTST.gif