What is in this leaflet
This leaflet answers some common questions about BORTEZOM Powder for Injection. It does not contain all the available information. It does not take the place of talking to your doctor or pharmacist.
All medicines have risks and benefits. Your doctor has weighed the risks of you being given BORTEZOM against the benefits this medicine is expected to have for you.
If you have any concerns about being given BORTEZOM ask your doctor.
Keep this leaflet while being treated.
You may need to read it again.
What BORTEZOM is used for
BORTEZOM belongs to a group of medicines called antineoplastic or cytotoxic medicines. You may also hear of these being called chemotherapy medicines. These medicines are used to kill cancer cells.
BORTEZOM is used to treat adults with multiple myeloma (cancer of the bone marrow). It is prescribed for patients who have not been previously treated for multiple myeloma. It is also prescribed for patients who have received one or more prior treatments and whose cancer is still progressing.
Your doctor may have prescribed BORTEZOM for another reason.
Ask your doctor if you have any questions about why BORTEZOM has been prescribed for you.
This medicine is available only with a doctor's prescription.
Before you are given BORTEZOM
When you must not use it:
Do not use BORTEZOM if:
- you know you are allergic (hypersensitive) to bortezomib or boron or mannitol.
Symptoms of an allergic reaction may include rash, itching or hives on the skin, shortness of breath, wheezing or difficulty breathing, swelling of the face, lips, tongue or other parts of the body.
Before you start to use it:
Tell your doctor if you have or have had any medical conditions, especially the following:
- blood disorder with a low level of red or white blood cells or platelets. This disorder may become worse during treatment with BORTEZOM.
- if you are suffering from diarrhoea or vomiting as this may become worse during treatment with BORTEZOM.
- a history of fainting, dizziness or light-headedness.
- kidney problems
- liver problems
- problems with numbness, tingling or pain in the hands or feet (neuropathy). This effect may be worsened by treatment with BORTEZOM.
- any bleeding problems
- problems with your heart
- lung or breathing problems
Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or intend to become pregnant.
Like most medicines used to treat cancer, BORTEZOM is not recommended for use during pregnancy.
Tell your doctor if you are breastfeeding or intend to breastfeed.
It is not known whether BORTEZOM passes into breast milk. Therefore there is a possibility that the breast- fed baby may be affected.
If you wish to restart breast-feeding after your BORTEZOM treatment, you must discuss this with your doctor or nurse, who will tell you when it is safe to do so.
Tell your doctor if you are trying to make your partner pregnant.
Both men and women receiving BORTEZOM and their partners must use a reliable method of contraception during and for 3 months after receiving BORTEZOM.
If you have not told your doctor about any of the above, tell them before you start treatment with BORTEZOM.
Taking other medicines:
Tell your doctor if you are taking any other medicines, including medicines you can buy without a prescription from a pharmacy, supermarket or health food shop.
In particular, tell your doctor if you are taking any of the following:
- amiodarone, a medicine used to treat irregular heart beat
- medicines used to treat viral infections such as flu, herpes and HIV
- isoniazid, a medicine used to treat tuberculosis
- nitrofurantoin, a medicine used to treat urinary tract infections
- medicines used to treat high cholesterol levels in the blood
- medicines used to treat diabetes
- medicines that may lower blood pressure
- rifampicin, an antibiotic used with other medicine to treat tuberculosis.
- medicine used to treat epilepsy such as carbamazepine and phenobarbital
- phenytoin, a medicine used in preventing seizures.
These medicines may be affected by BORTEZOM or may affect how well BORTEZOM works. Your doctor or pharmacist can tell you what to do if you are using any of these medicines.
How BORTEZOM is given
Your treatment with BORTEZOM will take place in a specialised medical unit, under the supervision of a doctor experienced in the use of cytotoxic medicinal products.
How much is given:
Your doctor will decide what dose you will receive. The dose will be calculated from your height and weight. It will also depend on factors such as kidney function, liver function and other medicines you are being given.
The safety of treatment with BORTEZOM in people with severe kidney function problems had not been well-studied.
The usual starting dose is 1.3 milligrams per square meter body surface area.
Your doctor may change the dose during treatment depending on your response.
Ask your doctor if you want to know more about the dose of BORTEZOM you receive.
How it is given:
BORTEZOM will be dissolved in sterile normal sodium chloride (salt) solution for injection. The solution is given as an injection into your vein (intravenously) over 3 to 5 seconds. The injection tube will be rinsed with a small quantity of sterile normal sodium chloride (salt) solution.
The solution can also be given subcutaneously as an injection into your thighs (right or left), or abdomen (right or left). BORTEZOM must be given intravenously or subcutaneously only. BORTEZOM must not be given into the space around the spinal cord (intrathecally).
When it is given:
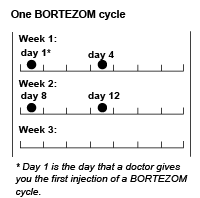
One cycle of treatment with BORTEZOM consists of a total of 4 doses given over 3 weeks. Doses are given on days 1, 4, 8 and 11 followed by a ten day break from the treatment.
When BORTEZOM is given with melphalan and prednisone, the treatment consists of a total of 9 cycles (54 weeks). In Cycles 1-4, BORTEZOM is administered twice weekly (days 1, 4, 8, 11, 22, 25, 29 and 32). In Cycles 5-9, BORTEZOM is administered once weekly (days (1, 8, 22 and 29).
When BORTEZOM is given with thalidomide and dexamethasone, the treatment consists of a total of 3 cycles (9 weeks) for the induction stage and 2 cycles (10 weeks) for the consolidation stage. During the induction stage, BORTEZOM is administered twice weekly (days 1, 4, 8 and 11). During the consolidation stage, BORTEZOM is administered once weekly (days 1, 8, 15 and 22).
When BORTEZOM is given with dexamethasone, the treatment consists of a total of 4 cycles (12 weeks). BORTEZOM will be administered twice weekly (days 1, 4, 8 and 11).
Your doctor will decide on the number of cycles of BORTEZOM needed. This will depend on how you respond to treatment.
What do I do if I receive too much? (overdose):
As BORTEZOM is given to you under the supervision of your doctor, it is very unlikely that you will receive too much. However if you experience any side effects after being given BORTEZOM, tell you doctor or nurse immediately or go to Accident and Emergencyat your nearest hospital.
You may need urgent medical attention.
While you are using BORTEZOM
Things you must do:
Be sure to keep all your doctor's appointments so your progress can be checked.
Your doctor will want to do some blood, urine and other tests from time to time to check on your progress and detect any unwanted side effects.
Keep follow up appointments with your doctor.
It is important to have your follow-up doses of BORTEZOM at the appropriate times to get the best effects from your treatment.
Be sure to follow up your doctor's instructions about other medicines you should take, and other things you should do.
You may need to take other medicines to help prevent unwanted effects of BORTEZOM. You may also need to drink extra fluids if you experience vomiting and/or diarrhoea. Ask your doctor or pharmacist if you have any questions.
Tell any other doctors, dentists and pharmacists who are treating you that you are having BORTEZOM.
If you are about to be started on any new medicines, tell your doctor, dentist or pharmacist that you are having BORTEZOM.
If you plan to have surgery, tell your doctor or dentist that you are having BORTEZOM.
If you become pregnant or yourpartner becomes pregnant while being given BORTEZOM, tell your doctor immediately. BORTEZOM can lower the number of white blood cells and platelets in your blood. This means that you have an increased chance of getting an infection or bleeding. The following precautions should be taken to reduce your risk of infection or bleeding:
- Avoid people who have infections. Check with your doctor immediately if you think you may be getting an infection, or if you get a fever, chills, cough, hoarse throat, lower back or side pain or find it’s painful or difficult to urinate.
- Be careful when using a toothbrush, toothpick or dental floss. Your doctor, dentist, nurse or pharmacist may recommend other ways to clean your teeth and gums. Check with your doctor before having any dental work.
- Be careful not to cut yourself when you are using sharp objects such as a razor or nail cutters.
Things to be careful of
Be careful driving or operating machinery until you know how BORTEZOM affects you.
BORTEZOM may cause tiredness, light-headedness, dizziness, fainting, double or blurred vision in some people. Make sure you know how you react to BORTEZOM before you drive a car, operate machinery, or do anything else that could be dangerous if you are dizzy, light headed or have double or blurred vision. If you drink alcohol, dizziness or light-headedness may be worse.
You may feel dizzy or faint when you get up quickly after sitting or lying down.
Getting up slowly may help.
Side Effects
Like all medicines, BORTEZOM can have side effects. Some of these effects may be serious. However there may be ways to reduce the discomfort of these effects. You may need medical treatment if you get some of the side effects.
Tell your doctor, nurse or pharmacist as soon as possible if you do not feel well while you are being treated with BORTEZOM.
Below is a list of the more common side effects you could get while being treated with BORTEZOM:
- tiredness, generally feeling unwell, weakness
- feeling sick (nausea) or vomiting
- diarrhoea
- constipation
- loss of appetite, and/or weight, fear of gaining weight
- bleeding or bruising more easily than normal
- sensitivity, numbness, tingling or burning sensation of the skin, or pain in the hands or feet
- fever, chills
- anaemia (a condition in which there is a decreased number of red blood cells)
- frequent infections such as fever, severe chills, sore throat or mouth ulcers
- headache
- trouble sleeping, sweating, anxiety, mood swings, confusion or depression
- painful, swollen joints
- pain in your limbs, back pain, bone pain, muscle cramps
- swelling (around the eyes or in the ankles, wrists, arms, legs or face)
- pins and needles and unpleasant sensations
- difficulty in breathing
- dizziness
- dehydration
- cough
- aching muscles, muscle tenderness or weakness not caused by exercise
- uncomfortable feeling in the stomach or belching after eating
- stomach pain
- bad taste in the mouth
- low blood pressure (dizziness, light headedness or fainting)
- chest pain
- small blisters in clusters on the skin (herpes)
- rash, itching
- redness of the skin or redness and pain at injection site
- blurred vision
- pneumonia
If you think you are having an allergic reaction to BORTEZOM, tell you doctor immediately or go to Accident and Emergency at your nearest hospital.
Symptoms usually include some or all of the following:
- rash, itching or hives on the skin
- shortness of breath, wheezing or difficulty breathing
- swelling of the face, lips, tongue or other parts of the body
Other side effects not listed above may also occur in some people.
Tell your doctor, nurse or pharmacist if you notice any other effect that is making you feel unwell.
Product Description
Storage
BORTEZOM should be kept in a cool dry place, protected from light, where the temperature stays below 25°C.
What it looks like:
BORTEZOM is a white to off- white powder in a glass vial.
Each pack contains one single-use vial.
Before injection, BORTEZOM powder is dissolved in a small quantity of sterile, sodium chloride solution. The solution for injection is clear and colourless.
BORTEZOM 3.5mg vial
(AUST R 214246)
Ingredients
Active ingredient:
- bortezomib 3.5 mg
(for BORTEZOM 3.5mg Vials)
Other ingredients:
- mannitol (E 421)
Sponsor
Pharmacor pty ltd. Chatswood, NSW, 2067
This leaflet was prepared in March 2022.
