What is in this leaflet
This leaflet answers some common questions about BUDENOFALK foam. It does not contain all the available information. It does not take the place of talking to your doctor or pharmacist.
All medicines have risks and benefits. Your doctor has weighed the risks of you using BUDENOFALK foam against the benefits they expect it will have for you.
If you have any concerns about using this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Keep this leaflet with the medicine. You may need to read it again.
What BUDENOFALK foam is used for
BUDENOFALK foam contains the active ingredient, budesonide. Budesonide belongs to a group of medications called corticosteroids. BUDENOFALK foam is used to treat ulcerative colitis (inflammation) of the rectum (back passage) and the lower part of the large bowel.
Ask your doctor if you have any questions about why this medicine has been prescribed for you. Your doctor may have prescribed it for another reason.
This medicine is not addictive.
This medicine is not expected to affect your ability to drive a car or operate machinery.
BUDENOFALK foam is only available on a doctor’s prescription.
There is not enough information to recommend the use of this medicine for children or adolescents.
Before you use it
When you must not use it
Do not use BUDENOFALK foam if you have an allergy to:
- any medicine containing budesonide
- any of the ingredients listed at the end of this leaflet.
Some symptoms of an allergic reaction may include shortness of breath, wheezing or difficulty breathing; swelling of the face, lips, tongue or other parts of the body; rash, itching or hives on the skin.
Do not use BUDENOFALK foam if you suffer from a severe liver disease (liver cirrhosis).
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date printed on the pack or if the packaging is torn or shows signs of tampering. If it has expired or is damaged, return it to your pharmacist for disposal.
If you are not sure whether you should start using this medicine, talk to your doctor.
Before you start to use it
Tell your doctor if you have any allergies to any other medicines, foods, preservatives or dyes.
Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant or are breastfeeding or wish to breastfeed. Your doctor will discuss the risks and benefits of using BUDENOFALK foam if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Tell your doctor if you have or have had any medical conditions, especially the following:
- liver disease
- lung disease (tuberculosis)
- high blood pressure
- diabetes, when the level of sugar in the blood is too high
- disease which causes bones to become less dense, gradually making them weaker, more brittle and likely to break (osteoporosis)
- ulcer in stomach or duodenum
- glaucoma (high pressure in the eye)
- cataracts
- family history of diabetes or glaucoma
- any infections
- any stresses
- any other disease where use of corticosteroids may have unwanted effects.
If you have not told your doctor about any of the above, tell him/her before you start using BUDENOFALK foam.
Contact your doctor if you have been exposed to chicken pox, measles and shingles. They may become more severe when you use BUDENOFALK foam.
Tell your doctor if you have not yet had measles.
If you know that you need to be vaccinated please speak to your doctor first.
If you know that you are due to have an operation please tell your doctor that you are using BUDENOFALK foam.
If you have been treated with a stronger corticosteroid preparation before starting treatment with BUDENOFALK foam, your symptoms may reappear when the medicine is changed.
If this happens, contact your doctor.
Contact your doctor if you experience blurred vision or other visual disturbances.
Taking other medicines
Tell your doctor if you are taking any other medicines, including any that you buy without a prescription from your pharmacy, supermarket or health food shop.
Some medicines and BUDENOFALK foam may interfere with each other. These include:
- cardiac glycosides such as digoxin, medicines used to treat heart conditions
- diuretics, medicines used to treat excess fluid in your body
- ketoconazole and itraconazole, medicines used to treat fungal infections
- antibiotics such as clarithromycin and rifampicin, medicines used to treat infections
- ritonavir and cobicistat medicines used for treating HIV infections
- carbamazepine, medicine used for treating epilepsy
- rifampicin, medicine used to treat tuberculosis
- contraceptive pill
- cholestyramine, medicine used to reduce cholesterol level
- cimetidine, medicine to reduce stomach acid.
These medicines may be affected by BUDENOFALK foam or may affect how well it works. You may need different amounts of your medicines, or you may need to use different medicines.
Avoid drinking grapefruit juice while you are taking BUDENOFALK foam as this can alter its effects.
Your doctor or pharmacist have more information on medicines to be careful with or avoid while using BUDENOFALK foam.
How to use it
Follow all directions given to you by your doctor or pharmacist carefully. They may differ from the information contained in this leaflet.
How much to use
Adults and the elderly:
Each BUDENOFALK foam can contains enough budesonide for 14 applications, or 2 weeks of dosing, based on a standard dose of 2 mg/day.
Apply one actuation daily, corresponding to 2 mg budesonide. BUDENOFALK 2 mg foam can be applied in the morning or evening.
How to use it
If possible, go to the toilet and empty your bowels before using the foam.
- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water.
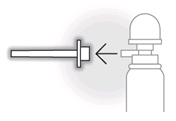
- Push the applicator firmly onto the spout of the spray can.
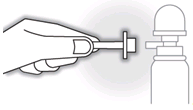
- Shake the can for 15 seconds to mix the contents.
- Each time you use a new can, remove the safety tab from under the pump dome.
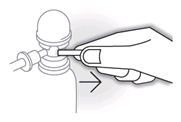
- Twist the dome on top of the canister until the semi-circular gap underneath it is in line with the nozzle.
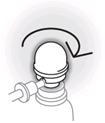
The spray can is now ready for use.
- Place your forefinger on top of the pump dome. Turn the spray can upside down. The pump dome must be pointing down.
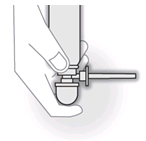
- Stand with one foot on the floor and raise the other foot onto a chair or stool.
- Insert the applicator into the rectum as far as comfortable. To administer a dose of BUDENOFALK foam, push the pump dome fully once with your finger and hold for 5 seconds then very slowly lift your finger off the pump dome. The foam is being delivered at this time and you must wait 15 seconds for dosing to be complete.
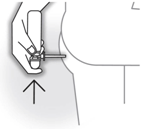
- Withdraw the applicator from the rectum slowly.
- Remove the applicator from the spout of the spray can and dispose of it in the plastic bag provided as domestic waste.
- Wash your hands thoroughly and try not to empty your bowels again for as long as possible.
You may experience a little discomfort and a feeling of urgency to empty your bowels immediately after foam insertion. This is normal and expected due to the inflammation present within the bowel. Try to resist this urge to empty your bowels for as long as possible. This feeling will subside as treatment continues and the inflammation decreases.
When to use it
Use your medicine at about the same time each day. Using it at the same time each day will have the best effect. It will help you remember when to use it.
How long to use it
The duration of treatment will be decided by your doctor. In general, the acute episode subsides after 6 to 8 weeks. After this you should stop using BUDENOFALK foam.
BUDENOFALK foam helps control your condition but does not cure it. Therefore, you must continue to use BUDENOFALK foam for as long as your doctor tells you to.
If you forget to use it
If it is almost time for your next dose, skip the dose you missed and take your next dose when you are meant to.
Otherwise, use it as soon as you remember and then go back to taking your medicine as you would normally.
Do not use a double dose to make up for the dose that you missed.
If you are not sure what to do, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
If you have trouble remembering when to use your medicine, ask your pharmacist for some hints.
If you use too much (overdose)
Immediately telephone your doctor or the Poisons Information Centre (telephone 13 11 26) for advice, or go to Accident and Emergency at the nearest hospital, if you think that you, or anyone else, may have used too much BUDENOFALK foam. Do this even if there are no signs of discomfort or poisoning. You may need urgent medical attention.
While you are using it
Things you must do
If you are about to be started on any new medicine, remind your doctor and pharmacist that you are using BUDENOFALK foam.
Tell any other doctors, dentists, and pharmacists who treat you that you are taking BUDENOFALK foam.
If you are going to have surgery, tell the surgeon or anaesthetist that you are taking BUDENOFALK foam. It may affect other medicines used during surgery.
If you become pregnant while taking BUDENOFALK foam, tell your doctor immediately.
Things that you must not do
Do not use BUDENOFALK foam to treat any other complaints unless your doctor tells you to.
Do not give your BUDENOFALK foam to anyone else, even if they have the same condition as you.
Do not stop using your BUDENOFALK foam or change the dosage without checking with your doctor.
Side effects
Tell your doctor or pharmacist as soon as possible if you do not feel well while you are using BUDENOFALK foam. Like all medicines, BUDENOFALK foam may have some side effects. Sometimes they are serious, most of the time they are not. You may need medical attention if you get some of the side effects.
Do not be alarmed by the following lists of side effects. You may not experience any of them.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist to answer any questions you may have.
Tell your doctor or pharmacist immediately if you notice any of the following:
- signs or symptoms of an infection
- headache
- changes in behaviour such as depression, irritability, euphoria, restlessness, anxiety or aggression.
Common side effects (that affect less than 1 in 10 patients):
- Burning or pain in the rectum
- Cushing’s syndrome – e.g. with roundness of the face, weight gain, reduced glucose tolerance, high blood sugar, high blood pressure, fluid retention in the tissues (e.g. swollen legs), increased excretion of potassium (hypokalaemia), irregular periods in women, unwanted body hair in women, impotence, abnormal laboratory findings (reduced adrenal function), red stripes on the skin (stretch marks), acne.
- indigestion, irritable stomach (dyspepsia)
- increased risk of infection
- muscle and joint pain, muscle weakness, muscle twitching
- brittle bones (osteoporosis)
- headache
- mood changes, such as depression, irritability or euphoria
- rash from hypersensitivity reactions, red spots from bleeding in the skin, delayed wound healing, local skin reactions such as contact dermatitis.
Uncommon side effects (that affect less than 1 in 100 patients):
- changes to the blood (increase in erythrocyte sedimentation rate, increase in the number of white blood cells)
- ulcers in the stomach or small intestine
- giddiness, disturbance of smell
- urinary tract infections
- sleeplessness, restlessness with increased physical activity, anxiety
- nausea, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, wind, tingling in the abdomen, anal fissure, mouth rash, urgent need to empty the bowels,rectal bleeding
- changes in liver function
- changes in pancreatic function, changes in adrenal hormones
- acne, increased sweating
- increase in appetite.
Rare side effects (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people):
- blurred vision
- inflammation of the pancreas
- bone loss due to poor circulation of blood (osteonecrosis)
- aggression
- bruising.
Very rare side effects (may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people):
- slowed growth in children
- constipation
- increased pressure in the brain, possibly with increased pressure in the eye (swelling of the optic disk) in adolescents
- increased risk of blood clotting, inflammation of the blood vessels (associated with stopping corticosteroid use after long-term therapy)
- tiredness, general feeling of being ill.
These side effects are typical of corticosteroid medications and most of them can also be expected for treatments with other corticosteroids. They may occur depending on your dose, duration of treatment, whether you have had or are having treatment with other corticosteroid preparations, and your individual susceptibility.
Some of these unwanted effects were only reported after long-term use of oral budesonide.
In general, the risk of side effects with BUDENOFALK foam is lower than with systemically acting (affecting the whole body) corticosteroid preparations due to its local action.
If you have been treated with a stronger corticosteroid preparation before starting treatment with BUDENOFALK foam, your symptoms may reappear when the medicine is changed.
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you notice anything else that is making you feel unwell. Other side effects not listed above may also occur in some patients.
After using it
Storage
Keep BUDENOFALK foam in its original packaging until it is time to use it.
Keep BUDENOFALK foam in a cool dry place where the temperature stays below 25°C.
Do not refrigerate or freeze. Protect from direct sunlight.
Keep away from flames or sparks. Contains flammable gas.
Use within 4 weeks of first opening.
Do not store BUDENOFALK foam or any other medicine in the bathroom or near a sink. Do not leave it on a window sill or in the car. Heat and dampness can destroy some medicines.
Keep it where children cannot reach it. A locked cupboard at least one-and-a-half metres above the ground is a good place to store medicines.
Disposal
If your doctor tells you to stop using BUDENOFALK foam or the expiry date has passed, ask your pharmacist what to do with any foam that is left over.
Do not pierce or burn the can even when empty.
Ingredients
Each dose/actuation of BUDENOFALK foam contains 2 mg of the active ingredient, budesonide.
Each container of BUDENOFALK foam also contains cetyl alcohol, emulsifying wax, purified water, disodium edetate, steareth-10, propylene glycol, citric acid monohydrate and butane, isobutane and propane as propellants.
Available in the following packs:
- One pressurised container with 14 applicators and 14 plastic bags
- Two pressurised containers, with 28 applicators and 28 plastic bags.
Not all pack sizes are currently available in Australia.
Plastic bags are for the hygienic disposal of the applicators.
Sponsor
Dr Falk Pharma Australia Pty Ltd, 815 Pacific Highway, Chatswood, NSW 2067
Australian Registration Number:
AUST R 179575
BUDENOFALK® is a registered trademark of Dr. Falk Pharma GmbH, Germany.
This leaflet was revised in November 2020
Published by MIMS February 2021

 Undesirable effects were reported in 14% of patients in clinical trials with Budenofalk foam. Burning in the rectum or pain were common, and nausea, headache and an increase in liver enzymes were uncommon.
Undesirable effects were reported in 14% of patients in clinical trials with Budenofalk foam. Burning in the rectum or pain were common, and nausea, headache and an increase in liver enzymes were uncommon.
 Scintigraphic study of a single rectal dose of 99mTc labelled budesonide 2 mg (Budenofalk) foam in 12 patients showed that the spread of the budesonide foam ranged between 11 and 40 cm (mean of 25.4 ± 10.3 cm) depending on the individual patient (this range includes from reaching the distal half of the sigmoid, to reaching the proximal third of the descending colon). The maximal spread was reached between 2 and 6 hours (mean of 4 hours) depending on the individual patient and remained relatively stable between 4 hours and 6 hours. The distal half sigmoid was reached in all patients on average after 2 hours and accounted for 27.4% of the radiolabelled budesonide foam at 2 hours.
Scintigraphic study of a single rectal dose of 99mTc labelled budesonide 2 mg (Budenofalk) foam in 12 patients showed that the spread of the budesonide foam ranged between 11 and 40 cm (mean of 25.4 ± 10.3 cm) depending on the individual patient (this range includes from reaching the distal half of the sigmoid, to reaching the proximal third of the descending colon). The maximal spread was reached between 2 and 6 hours (mean of 4 hours) depending on the individual patient and remained relatively stable between 4 hours and 6 hours. The distal half sigmoid was reached in all patients on average after 2 hours and accounted for 27.4% of the radiolabelled budesonide foam at 2 hours. Chemical name: 16α,17α-butylidene dioxy-11β, 21-dihydroxy-1,4-pregnadiene-3, 20-dione C25H34O6 = 430.5.
Chemical name: 16α,17α-butylidene dioxy-11β, 21-dihydroxy-1,4-pregnadiene-3, 20-dione C25H34O6 = 430.5.