COPAXONE® 40 mg/mL Pre-filled Syringe
| Consumer Medicine Information (CMI) summary |
The full CMI on the next page has more details. If you are worried about using this medicine, speak to your doctor or pharmacist.
| 1. Why am I using COPAXONE? |
COPAXONE contains the active ingredient glatiramer acetate. COPAXONE is used for the management of relapsing forms of Multiple Sclerosis (MS).
For more information, see Section 1. Why am I using COPAXONE? in the full CMI.
| 2. What should I know before I use COPAXONE? |
Do not use if you have ever had an allergic reaction to glatiramer acetate or any of the ingredients listed at the end of the CMI.
Talk to your doctor if you have any other medical conditions, take any other medicines, or are pregnant or plan to become pregnant or are breastfeeding.
For more information, see Section 2. What should I know before I use COPAXONE? in the full CMI.
| 3. What if I am taking other medicines? |
Some medicines may interfere with COPAXONE and affect how it works.
For more information, see Section 3. What if I am taking other medicines? in the full CMI.
| 4. How do I use COPAXONE? |
- The recommended dose of COPAXONE is one 40 mg/mL pre-filled syringe (1mL) injected three times a week and at least 48 hours apart.
- COPAXONE 40 mg/mL is given by an injection into the fatty layer under the skin (subcutaneous injection).
More instructions can be found in Section 4. How do I use COPAXONE? in the full CMI.
| 5. What should I know while using COPAXONE? |
| Things you should do |
|
| Things you should not do |
|
| Looking after your medicine |
|
For more information, see Section 5. What should I know while using COPAXONE? in the full CMI.
| 6. Are there any side effects? |
Common side effects: Immediate Post Injection Reaction which includes the following symptoms - reddening of the face and/or neck, chest pain or tightness, feeling your heart beat quickly (heart palpitations), anxiety and difficulty in breathing.
Serious side effects: Symptoms of an allergic reaction that include - swelling of the face, lips, mouth or throat, which may cause difficultly in swallowing or breathing, hives, chest pain, trouble breathing and severe pain, redness or swelling at the injection site that does not go away.
For more information, including what to do if you have any side effects, see Section 6. Are there any side effects? in the full CMI.
COPAXONE® 40 mg/mL Pre-filled Syringe Solution for Injection
Active ingredient(s): glatiramer acetate
| Consumer Medicine Information (CMI) |
This leaflet provides important information about using COPAXONE. You should also speak to your doctor or pharmacist if you would like further information or if you have any concerns or questions about using COPAXONE.
Where to find information in this leaflet:
1. Why am I using COPAXONE?
2. What should I know before I use COPAXONE?
3. What if I am taking other medicines?
4. How do I use COPAXONE?
5. What should I know while using COPAXONE?
6. Are there any side effects?
7. Product details
| 1. Why am I using COPAXONE? |
COPAXONE contains the active ingredient glatiramer acetate. The exact mechanism of how COPAXONE works is unknown, it is thought that COPAXONE works by changing the immune processes that are believed to be responsible for the disease.
COPAXONE is used for the management of relapsing forms of Multiple Sclerosis (MS).
COPAXONE may also be used in patients who, for the first time, have experienced symptoms and have MRI changes that indicate a high risk for development of MS. Your doctor will rule out any other reasons which could explain these symptoms before you are treated.
The cause of MS is not yet known. MS affects the brain and spinal cord. In MS, the body's immune system reacts against its own myelin (the ‘insulation’ surrounding nerve fibres). In relapsing forms of MS, people can have ‘exacerbations’ from time to time (e.g. blurred vision, weakness in the legs or arms, or loss of control of bowel or bladder function). These are followed by periods of recovery.
COPAXONE has been shown to be effective in reducing the number of relapses in patients with relapsing remitting MS. Although it is not a cure, patients treated with COPAXONE 40mg/mL generally find that they will experience fewer relapses.
| 2. What should I know before I use COPAXONE? |
Warnings
Do not use COPAXONE if:
- you are allergic to glatiramer acetate, or any of the ingredients listed at the end of this leaflet.
- Always check the ingredients to make sure you can use this medicine.
Check with your doctor if you:
- have any other medical conditions including asthma and liver disease
- take any medicines for any other condition
- have ever had asthma
- have a history of severe allergic reactions
- have ever had a liver injury
- plan to have surgery
During treatment, you may be at risk of developing certain side effects. It is important you understand these risks and how to monitor for them. See additional information under Section 6. Are there any side effects?
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Check with your doctor if you are pregnant or intend to become pregnant.
Limited data in humans showed no negative effects of glatiramer acetate on breastfed infants.
Talk to your doctor if you are breastfeeding or intend to breastfeed.
Children
Do not give COPAXONE to children. There is no experience with its use in children under 12 years of age.
| 3. What if I am taking other medicines? |
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking any other medicines, including any medicines, vitamins or supplements that you buy without a prescription from your pharmacy, supermarket or health food shop.
Some medicines may interfere with COPAXONE and affect how it works.
Some medicines may interfere with the absorption of COPAXONE.
Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure about what medicines, vitamins or supplements you are taking and if these affect COPAXONE.
| 4. How do I use COPAXONE? |
How much to use
- The recommended dose of COPAXONE is one 40 mg/ mL pre-filled syringe (1mL) injected three times a week and at least 48 hours apart.
- Follow the instructions provided and use COPAXONE until your doctor tells you to stop.
When to use COPAXONE
- COPAXONE 40 mg/mL should be used, if possible, at the same time and on the same three days each week (for example, Monday, Wednesday and Friday) at least 48 hours apart.
- Do not change the dose or dosing schedule or stop using COPAXONE without talking to your doctor.
How to use COPAXONE
- COPAXONE 40 mg/mL is given by an injection into the fatty layer under the skin (subcutaneous injection).
- Many people with MS learn to give themselves the injection or have it given by a carer.
- Self-injection needs to be taught and practiced. It is important that a qualified healthcare professional supervises your first injection.
- Your doctor may teach you to self-inject or arrange for an MS education nurse to do so.
- You may have a friend attend the injection training session as your assistant. Especially when you first start giving yourself injections, your assistant should be with you.
- Talk to your doctor or the MS Society or telephone 1800 502 802 in Australia or 0800 502 802, in New Zealand for more information.
- Patient support kits that include a self-injection device are available by telephoning 1800 502 802 in Australia or 0800 502 802, in New Zealand
- After being taught to self-inject, you can refer to this leaflet for step-by-step instructions about how to prepare and inject COPAXONE 40 mg/mL.
- The following instructions explain how to inject COPAXONE 40 mg/mL yourself.
- Do not attempt self-injection until you are confident that you understand how to inject yourself.
- Please read these instructions carefully.
Before you inject
- COPAXONE 40 mg/mL pre-filled syringe is pre-mixed and ready for you to use.
- Make sure that the blister with the syringe inside is taken out of the refrigerator for 20 minutes before you use it.
It is important that the solution is at room temperature when you inject it. If you need to delay your injection, return the blister to its package in the refrigerator.
Always inspect COPAXONE solution in the pre-filled syringe before you use it. Do not inject the solution if it is cloudy or has particles in it.
Gathering the Materials
Gather the following items on a towel that is laid on a flat surface in a clean, well-lit area:
- One blister with COPAXONE 40 mg/mL pre-filled syringe (at room temperature - as described above)
- A dry cotton ball
- Disposal unit for used syringes
Wash and dry your hands. Do not touch your hair or skin afterwards. This will help prevent infection.
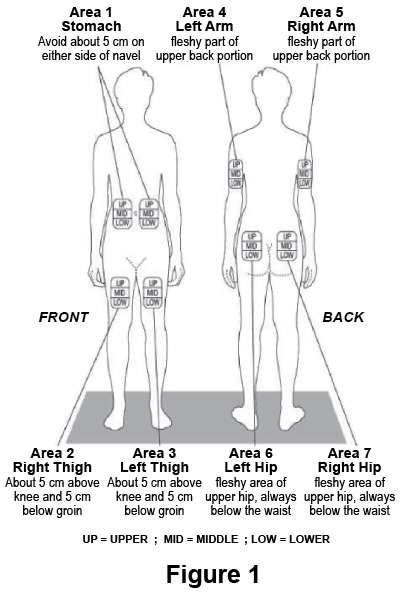
Deciding where to Inject
There are seven injection areas on your body; arms, thighs, back of the hips and stomach (belly). Within each injection area there are multiple injection sites (Figure 1).
Rotate the injection sites within an area.
You should not use any site more than once a week. Choose a different site for each injection. This will reduce the likelihood of irritation, pain or loss of fatty tissue (lipoatrophy) at the site of injection.
Marking a calendar will help you keep track of the sites you have used each week.
Do not inject in an area of skin that is bruised, inflamed or damaged.
Giving yourself the injection
- Remove the syringe from its protective blister by peeling back the blister foil.
- Pick up the syringe as you would a pencil, using the hand you write with. Remove the plastic cover from the needle.
- Pinch about a 5 cm fold of skin between thumb and index finger.
When you inject in the upper back portions of your arms, it is not possible to pinch 5 cm of skin with one hand and inject yourself with the other hand. Ask your doctor / nurse for instruction on how to use these areas.
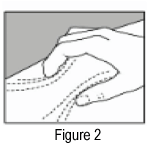
- Insert the needle into the 5 cm fold of skin. It may help to steady your hand by resting the heel of your hand against your body.
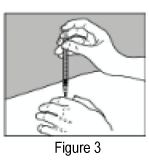
- When the needle is all the way in, release the fold of skin.
- Inject the medication by holding the syringe steady while pushing down on the plunger until the syringe is empty. The injection should take just a few seconds.
- Pull the needle straight out.
- Press a dry cotton ball on the injection site for a few seconds, but do not massage it.
- Dispose of the pre-filled syringe in a safe hard-walled container, according to your doctor's instructions and the laws of your state (if any). Ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice if you are in doubt.
Do not reuse the pre-filled syringe. Each pre-filled syringe should be used only for one injection.
Some patients may experience a side-effect known as the Immediate Post Injection Reaction. See Section 6. Are there any side effects?
If you forget to use COPAXONE
COPAXONE should be used regularly at the same time and on the same three days each week. If you miss your dose at the usual time, you should take your next dose as soon as you remember or are able to take it, then skip the following day. If possible, you should return to your regular administration schedule the following week.
Do not take a double dose to make up for the dose you missed.
If you use too much COPAXONE
If you think that you have used too much COPAXONE, you may need urgent medical attention.
You should immediately:
- phone the Poisons Information Centre
(by calling 13 11 26 in Australia or 0800 764 766 in New Zealand), or - contact your doctor, or
- go to the Emergency Department at your nearest hospital.
You should do this even if there are no signs of discomfort or poisoning.
| 5. What should I know while using COPAXONE? |
Things you should do
If you are about to be started on any new medicine, tell your doctor and pharmacist that you are using COPAXONE 40 mg/mL.
If you plan to have surgery that needs a general anaesthetic, tell your doctor or dentist that you are using this medicine.
If you become pregnant while you are using this medicine, talk to your doctor to discuss whether ongoing COPAXONE treatment is appropriate for you.
Remind any doctor, dentist or pharmacist you visit that you are using COPAXONE.
Things you should not do
- Do not use more than the recommended dose unless your doctor tells you to.
- Do not give this medicine to anyone else, even if they have the same condition as you.
Looking after your medicine
- Keep COPAXONE 40 mg/mL pre-filled syringes in the refrigerator at 2°C to 8°C.
- Keep COPAXONE 40 mg/mL in the pack until it is time to use it. Protect from direct light.
- In the event of refrigeration being unavailable, COPAXONE 40 mg/mL may be stored below 25°C on one occasion for up to one month.
- COPAXONE 40 mg/mL must not be frozen. Do not place in the freezer or freezing compartment of a refrigerator.
Follow the instructions in the carton on how to take care of your medicine properly.
Store it in a cool dry place away from moisture, heat or sunlight; for example, do not store it:
- in the bathroom or near a sink, or
- in the car or on window sills.
Keep it where young children cannot reach it.
When to discard your medicine
Ask your doctor or nurse about obtaining a “sharps container”.
After use, place all used syringes and needles in a hard-walled plastic container, such as a liquid laundry detergent container or sharps container.
It is very important that you keep the cover of the container tightly shut and that you store it out of the reach of children. When the container is full, check with your doctor or nurse about proper disposal.
Getting rid of any unwanted medicine
If you no longer need to use this medicine or it is out of date, take it to any pharmacy for safe disposal.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date.
| 6. Are there any side effects? |
All medicines can have side effects. If you do experience any side effects, most of them are minor and temporary. However, some side effects may need medical attention.
See the information below and, if you need to, ask your doctor or pharmacist if you have any further questions about side effects.
Less serious side effects
| Less serious side effects | What to do |
Skin related:
| Speak to your doctor if you have any of these less serious side effects and they worry you. |
Serious side effects
| Serious side effects | What to do |
Symptoms of an allergic reaction:
| Call your doctor straight away, or go straight to the Emergency Department at your nearest hospital if you notice any of these serious side effects. |
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you notice anything else that may be making you feel unwell.
Other side effects not listed here may occur in some people.
Reporting side effects
After you have received medical advice for any side effects you experience, you can report side effects to the Therapeutic Goods Administration at www.tga.gov.au/reporting-problems. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
Always make sure you speak to your doctor or pharmacist before you decide to stop taking any of your medicines.
| 7. Product details |
This medicine is only available with a doctor's prescription.
What COPAXONE contains
| Active ingredient (main ingredient) | Glatiramer acetate 40 mg/mL |
| Other ingredients (inactive ingredients) | Mannitol Water for Injections |
Do not take this medicine if you are allergic to any of these ingredients.
What COPAXONE looks like
COPAXONE 40 mg/mL is a clear colourless solution supplied in 1mL glass single use pre-filled syringes fitted with a staked inch needle (Aust R 218615).
COPAXONE 40 mg/mL pre-filled syringe is supplied in a box of 12 blister packed pre-filled syringes.
Who distributes COPAXONE
COPAXONE 40 mg/mL is distributed in Australia by:
Teva Pharma Australia Pty Ltd
Level 1, 37 Epping Road
Macquarie Park NSW 2113
COPAXONE 40 mg/mL is distributed in New Zealand by:
Teva Pharma (New Zealand) Limited
PO Box 128 244
Remuera
Auckland 1541
This leaflet was prepared in March 2023.
® Copaxone is a registered trademark of Teva Pharmaceuticals Industries Ltd.
Published by MIMS May 2023
