Consumer medicine information
Dolased Forte Tablets
Paracetamol + Codeine phosphate hemihydrate + Doxylamine succinate
BRAND INFORMATION
Brand name
Dolased Forte
Active ingredient
Paracetamol + Codeine phosphate hemihydrate + Doxylamine succinate
Schedule
S4
Dolased Forte Tablets
Boxed Warnings
1 Name of Medicine
Paracetamol, codeine phosphate hemihydrate and doxylamine succinate.
2 Qualitative and Quantitative Composition
For the full list of excipients, see Section 6.1 List of Excipients.
3 Pharmaceutical Form
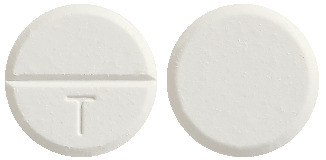
Each tablet contains paracetamol 450 mg, codeine phosphate hemihydrate 30 mg, doxylamine succinate 5 mg. Tablets are round flat, white uncoated with bevelled edge with 'T' on one side of a break-bar.
4 Clinical Particulars
4.9 Overdose
For information on the management of overdose, contact the Poisons Information Centre on 13 11 26 (Australia).
Overdose, 7.5 g (17 Dolased Forte tablets) or more of paracetamol in a single administration in adults or 140 mg/kg of body weight in a single administration in children, causes cytolytic hepatitis likely to induce complete and irreversible hepatic necrosis, resulting in acute or fulminant hepatic failure, hepatocellular insufficiency, metabolic acidosis and encephalopathy which may lead to coma and death.
Nausea, vomiting, anorexia, pallor and abdominal pain generally appear during the first 24 hours of overdosage with paracetamol. Overdosage with paracetamol may cause hepatic cytolysis which can lead to hepatocellular insufficiency, gastrointestinal bleeding, metabolic acidosis, encephalopathy, disseminated intravascular coagulation, coma and death. Increased levels of hepatic transaminases, lactate dehydrogenase and bilirubin with a reduction in prothrombin level can appear 12 to 48 hours after acute overdosage. It can also lead to pancreatitis, acute renal failure and pancytopenia.
Reactions associated with doxylamine succinate overdosage may vary from central nervous depression to stimulation. Stimulation is particularly likely in children. Atropine-like signs and symptoms: dry mouth; fixed, dilated pupils; flushing and gastrointestinal symptoms may also occur. Severe rhabdomyolysis after doxylamine succinate overdose has been reported in humans.
In an evaluation of codeine intoxication in children, symptoms ranked by decreasing order of frequency included: sedation, rash, miosis, vomiting, itching, ataxia and swelling of the skin. Respiratory failure may occur. Blood concentrations of codeine ranged from 1.4 to 5.6 micrograms per mL in eight adults whose deaths were attributed to codeine overdosage.
The ingestion of very high doses of codeine can cause initial excitation, anxiety, insomnia followed by drowsiness in certain cases, areflexia progressing to stupor or coma, headache, miosis, alterations in blood pressure, arrhythmias, dry mouth, hypersensitivity reactions, cold clammy skin, bradycardia, tachycardia, convulsions, gastrointestinal disorders, nausea, vomiting and respiratory depression.
Severe intoxication can lead to apnoea, circulatory collapse, cardiac arrest and death.
Consists primarily of management of paracetamol toxicity; naloxone hydrochloride is the treatment of choice for codeine intoxication and must be administered intravenously. In cases of overdosage, methods of reducing the absorption of ingested drug are important. Prompt administration of 50 g activated charcoal and 500 mL iced mannitol 20% by mouth may reduce absorption.
Determinations of the plasma concentration of paracetamol are recommended. Plasma concentrations of paracetamol should be measured at 4 hours or later after ingestion (earlier concentrations are unreliable).
If the history suggests that 15 g paracetamol or more has been ingested, administer one of the following antidotes.
If more than ten hours have elapsed since the overdosage was taken, the antidote may be ineffective.
In general, treatment for codeine overdose should be symptomatic: re-establish adequate respiratory exchange by ensuring a clear airway and using mechanical ventilation. When treatment for paracetamol toxicity has been initiated; naloxone 400 microgram may be administered SC, IM or IV; IV may be repeated at intervals of 2 to 3 minutes if necessary. Assisted respiration may be required.
Further measures will depend on the severity, nature and course of clinical symptoms of intoxication and should follow standard intensive care protocols.
Overdosage and toxicity (including death) have been reported in children younger than 2 years of age receiving preparations containing antihistamines (including doxylamine), cough suppressants, expectorants, and nasal decongestants alone or in combination for relief of symptoms of upper respiratory tract infection.
5 Pharmacological Properties
5.3 Preclinical Safety Data
6 Pharmaceutical Particulars
6.7 Physicochemical Properties
https://stagingapi.mims.com/au/public/v2/images/fullchemgif/CSPARCET.gif
Molecular formula: C8H9NO2.
Molecular Weight: 151.20.
Paracetamol: White to almost white crystalline powder. Paracetamol is sparingly soluble in water, freely soluble in alcohol, very slightly soluble in methylene chloride.
https://stagingapi.mims.com/au/public/v2/images/fullchemgif/CSCOPHHE.gif
Molecular formula: C18H24NO7P.½H2O.
Molecular Weight: 406.4.
Codeine phosphate hemihydrate: White to almost white crystalline powder or small, colourless crystals. Freely soluble in water, slightly soluble or very slightly soluble in ethanol (96%). Melting point - 238-240°C.
https://stagingapi.mims.com/au/public/v2/images/fullchemgif/CSDOXSUC.gif
Molecular formula: C21H28N2O5.
Molecular Weight: 388.47.
Doxylamine succinate: White to creamy white crystalline powder with a characteristic odour. Very soluble in water and freely soluble in alcohol.
7 Medicine Schedule (Poisons Standard)
Prescription Only Medicine (Schedule 4).
Summary Table of Changes
https://stagingapi.mims.com/au/public/v2/images/fulltablegif/DOLFORST.gif