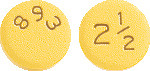Notes
Distributed by Pfizer Australia Pty Ltd
1 Name of Medicine
Apixaban.
2 Qualitative and Quantitative Composition
Each 2.5 mg film-coated tablet contains 2.5 mg apixaban.
Each 5 mg film-coated tablet contains 5 mg apixaban.
List of excipients with known effect. Lactose.
For the full list of excipients, see Section 6.1.
3 Pharmaceutical Form
Film-coated tablets.
Eliquis containing 2.5 mg apixaban for oral administration is available as yellow round, biconvex, film-coated tablets debossed with "893" on one side and "2½" on the other side.
Eliquis containing 5 mg apixaban for oral administration is available as pink oval-shaped, biconvex, film-coated tablets debossed with "894" on one side and "5" on the other side.
4 Clinical Particulars
4.9 Overdose
For information on the management of overdose, contact the Poison Information Centre on 131126 (Australia).
For situations when reversal of anticoagulation is needed due to life-threatening or uncontrolled bleeding, a reversal agent for factor Xa inhibitors is available (see Section 4.4, Haemorrhage risk).
Overdose of Eliquis may result in a higher risk of bleeding. In the event of haemorrhagic complications, the source of bleeding needs to be investigated and appropriate symptomatic treatment initiated (see Section 4.4, Haemorrhage risk).
In controlled clinical trials, orally administered apixaban in healthy subjects at doses up to 50 mg daily for 3 to 7 days (25 mg twice a day for 7 days or 50 mg once a day for 3 days) had no clinically relevant adverse effects.
Administration of activated charcoal may be useful in the management of apixaban overdose or accidental ingestion. In patients who are not fully conscious or have impaired gag reflex, consideration should be given to administering activated charcoal via a nasogastric tube, once the airway is protected, given the high incidence of gastrointestinal side effects, such as vomiting, associated with activated charcoal. Healthcare professionals are encouraged to review the activated charcoal product information for further information pertaining to the administration of activated charcoal.
A nonclinical study in dogs demonstrated that oral administration of activated charcoal suspended in water up to 3 hours after apixaban administration reduced apixaban exposure.
Eighteen healthy subjects were enrolled in a study to assess the effect of activated charcoal with sorbitol on the pharmacokinetics of a single 20 mg dose of apixaban. This was a three treatment, three period, randomised, crossover study where the subjects received a dose of apixaban alone, or followed by the administration of activated charcoal with sorbitol 2 and 6 hours after ingestion of the apixaban dose. The administration of activated charcoal with sorbitol 2 and 6 hours after apixaban reduced mean apixaban AUC by 50% and 27%, respectively, and had no impact on Cmax. Mean half-life of apixaban decreased from 13.4 hours when apixaban was administered alone to 5.3 hours and 4.9 hours, respectively, when activated charcoal with sorbitol was administered 2 and 6 hours after apixaban.
Haemodialysis decreased apixaban AUC by 14% in subjects with endstage renal disease, when a single dose of apixaban 5 mg was administered orally. Therefore, haemodialysis is unlikely to be an effective means of managing apixaban overdose (see Section 5.2 Pharmacokinetic Properties, Special populations, Renal impairment).
Management of bleeding. In the event of hemorrhagic complications in a patient receiving Eliquis, treatment must be discontinued, and the source of bleeding investigated. Appropriate standard treatment, e.g. surgical hemostasis as indicated and blood volume replacement, should be undertaken. In addition, consideration may be given to the use of fresh whole blood or the transfusion of fresh frozen plasma.
For situations when reversal of anticoagulation is needed due to life threatening or uncontrolled bleeding, a reversal agent for factor Xa inhibitors is available. Administration of prothrombin complex concentrates (PCCs) or recombinant factor VIIa may also be considered.
Redosing of prothrombin complex concentrate, activated prothrombin complex concentrate, or recombinant factor VIIa could be considered and titrated depending on improvement of bleeding.
However, these agents have not been evaluated in clinical studies.
5 Pharmacological Properties
5.3 Preclinical Safety Data
Genotoxicity. Apixaban did not induce gene mutations in bacteria (Salmonella typhimurium) or chromosomal damage in mammalian cells (Chinese hamster ovary cells) in vitro and lymphocytes in rats in vivo. There was no evidence of genotoxic potential in a micronucleus test in rats. The oral doses in the rat lymphocyte chromosome aberration study at up to 600 mg/kg/day for 30 days resulted in plasma apixaban concentrations 4 times the human exposure at 5 mg twice daily based on free fraction Cmax.
Carcinogenicity. Long-term studies in mice and rats at dietary doses up to 1500 and 600 mg/kg/day, respectively, did not show any evidence of carcinogenic potential. These doses resulted in plasma apixaban concentrations 42 times (mice) and 8 times (rat) human values at 2.5 mg twice daily, or 9 to 21 times (mouse) and 3 times (rat) human values at 5 mg twice daily based on free fraction AUC.
6 Pharmaceutical Particulars
6.7 Physicochemical Properties
Apixaban, a selective inhibitor of the coagulation factor Xa (FXa), is chemically described as 1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-7-oxo- 6-[4-(2-oxopiperidin-1-yl)phenyl]- 4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1H-pyrazolo [3,4-c]pyridine-3-carboxamide. Its molecular formula is C25H25N5O4, which corresponds to a molecular weight of 459.5. Apixaban has the following structural formula:
Chemical structure.
https://stagingapi.mims.com/au/public/v2/images/fullchemgif/CSAPIXAB.gif CAS number. 503612-47-3.
Apixaban is a white to pale yellow powder. At physiological pH (1.2-6.8), apixaban does not ionize; its aqueous solubility across the physiological pH range is ~ 0.04 mg/mL. The octanol/water partition coefficient is 44.7 at pH 7.4.
7 Medicine Schedule (Poisons Standard)
S4 - Prescription Only Medicine.
Summary Table of Changes
https://stagingapi.mims.com/au/public/v2/images/fulltablegif/ELIQUIST.gif