What is in this leaflet
This leaflet answers some common questions about Estrogel.It does not contain all the available information. It does not take the place of talking to your pharmacist or doctor.
All medicines have risks and benefits. Your pharmacist or doctor has weighed the risks of you taking Estrogel against the benefits they expect it will have for you.
If you have any concerns about taking this medicine, ask your pharmacist or doctor.
Keep this leaflet with the medicine.
You may need to read it again.
What Estrogel is used for
Estrogel is a Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT). It contains the female hormone estrogen. Estrogel is used in postmenopausal women who have not had a natural period within the last 6 months.
Estrogel is used for:
Relief of symptoms occurring after menopause
During menopause, the amount of the estrogen produced by a woman’s body drops. This can cause symptoms such as hot face, neck and chest (“hot flushes”). Estrogel alleviates these symptoms after menopause. You will only be prescribed Estrogel if your symptoms seriously hinder your daily life.
Prevention of osteoporosis
After menopause some women may develop fragile bones (osteoporosis). You should discuss all available options with your doctor.
If you are at an increased risk of fractures due to osteoporosis and other medicines are not suitable for you, you can use Estrogel to prevent osteoporosis after menopause.
Estrogel works by replacing the estrogen in your body. This is so that you have a similar amount of estrogen as before your menopause.
Ask your doctor if you have any questions about why this medicine has been prescribed for you.
Your doctor may have prescribed it for another reason.
Before you use Estrogel
When you must not use it
Do not use Estrogel if you have an allergy to:
- any medicine containing estradiol
- any of the ingredients listed at the end of this leaflet.
Some of the symptoms of an allergic reaction may include:
- shortness of breath
- wheezing or difficulty breathing
- swelling of the face, lips, tongue or other parts of the body
- rash, itching or hives on the skin
Do not use this medicine if you have any of the following conditions:
- If you have or have ever had breast cancer, or if you are suspected of having it,
- If you have cancer which is sensitive to estrogen, such as cancer of the womb lining (endometrium), or if you are suspected of having it,
- If you have any unexplained vaginal bleeding,
- If you have excessive thickening of the womb lining (endometrial hyperplasia) that is not being treated,
- If you have or have ever had blood clots in a vein (thrombosis), such as in the legs (deep venous thrombosis) or lungs (pulmonary embolism),
- If you have a blood clotting disorder (such as protein C, protein S, or antithrombin deficiency),
- If you have or recently have had a disease caused by blood clots in the arteries, such as a heart attack, stroke or angina,
- If you have or have ever had a liver disease and your liver function tests have not returned to normal,
- If you have a rare blood problem called “porphyria” which is passed down in families (inherited).
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date printed on the pack or if the packaging is torn or shows signs of tampering.
If it has expired or is damaged, return it to your pharmacist for disposal.
If you are not sure whether you should start using this medicine, talk to your doctor.
Before you start to use it
Tell your doctor if you have allergies to any other medicines, foods, preservatives or dyes.
Tell your doctor if you have or have had any of the following medical conditions, as these may return or become worse during treatment with Estrogel:
- liver or kidney disease
- difficulty breathing, wheezing, chronic cough, asthma or other chronic breathing conditions
- fibrosis inside your womb,
- growth of womb lining outside your womb (endometriosis) or a history of excessive growth of the womb lining (endometrial hyperplasia),
- increased risk of developing blood clots (see “Blood clots in a vein (thrombosis)”),
- increased risk of getting an estrogen-sensitive cancer (such as having a mother, sister or grandmother who has had breast cancer),
- high blood pressure,
- a liver disorder, such as a benign liver tumour,
- diabetes,
- gallstones,
- migraine or severe headaches,
- a disease of the immune system that affects many organs of the body (Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, SLE),
- epilepsy,
- asthma,
- a disease affecting the eardrum and hearing (otosclerosis),
- a very high level of fat in your blood (triglycerides),
- fluid retention due to heart or kidney problems,
- if you receive thyroid hormone therapy.
- if you have hereditary or acquired angioedema.
Stop using Estrogel and see a doctor immediately
If you notice any of the following when taking HRT:
- yellowing of your skin or the whites of your eyes (jaundice). These may be signs of a liver disease
- a large rise in your blood pressure (symptoms may be headache, tiredness, dizziness)
- migraine-like headaches which happen for the first time
- if you become pregnant
- if you notice signs of a blood clot, such as: painful swelling and redness of the legs, or sudden chest pain
- difficulty in breathing
Note: Estrogel is not a contraceptive. If it is less than 12 months since your last menstrual period or you are under 50 years old, you may still need to use additional contraception to prevent pregnancy. Speak to your doctor for advice.
HRT and cancer
Excessive thickening of the lining of the womb (endometrial hyperplasia) and cancer of the lining of the womb (endometrial cancer)
Using estrogen-only HRT will increase the risk of excessive thickening of the lining of the womb (endometrial hyperplasia) and cancer of the womb lining (endometrial cancer).
Using a progestogen (eg. progesterone) in addition to the estrogen for at least 12 days of each 28 day cycle protects you from this extra risk. Your doctor will prescribe a progestogen separately if you still have your womb. If you have had your womb removed (a hysterectomy), discuss with your doctor whether you can safely take this product without a progestogen.
In women who still have a womb and who are not using HRT, on average 5 in 1000 will be diagnosed with endometrial cancer between the ages of 50 and 65.
For women aged 50 to 65 who still have a womb and who take estrogen-only HRT, between 10 and 60 women in 1000 will be diagnosed with endometrial cancer (i.e. between 5 and 55 extra cases), depending on the dose and for how long it is taken.
Irregular bleeding
You may have irregular bleeding or drops of blood (spotting) during the first 3-6 months of using Estrogel. However, if the irregular bleeding:
- carries on for more than the first 6 months
- starts after you have been using Estrogel for more than 6 months
- carries on after you have stopped using Estrogel see your doctor as soon as possible.
Breast cancer
Evidence shows that using combined estrogen-progestogen or estrogen-only HRT increases the risk of breast cancer. The extra risk depends on how long you use HRT. The additional risk becomes clear within 3 years of use. After stopping HRT, the extra risk will decrease with time, but the risk may persist for 10 years or more if you have used HRT for more than 5 years.
Compare
Women aged 50 to 54 who are not taking HRT, on average 13 to 17 in 1000 will be diagnosed with breast cancer over a 5-year period.
For women aged 50 who start taking estrogen only HRT for 5 years there will be 16-17 cases in 1000 users (i.e. an extra 0 – 3 cases).
For women aged 50 who start taking estrogen-progestogen HRT over 5 years, there will be 21 cases in 1000 users (i.e. an extra 4 to 8 cases).
For women aged 50 -59 who are not taking HRT, on average 27 in 1000 will be diagnosed with breast cancer over a 10 year period.
For women aged 50 who start taking estrogen only HRT for 10 years there will be 34 cases in 1000 users (i.e. an extra 7 cases).
For women aged 50 who start taking estrogen-progestogen HRT over 10 years, there will be 48 cases in 1000 users (i.e. an extra 21 cases).
Regularly check your breasts. See your doctor if you notice any changes such as:
- dimpling of the skin
- changes in the nipple
- any lumps you can see or feel.
Additionally, you are advised to join mammography screening programs when offered to you. For mammogram screening, it is important that you inform the nurse/healthcare professional who is actually taking the x-ray that you use HRT, as this medication may increase the density of your breasts which may affect the outcome of the mammogram. Where the density of the breast is increased, mammography may not detect all lumps.
Ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer is rare, much rarer than breast cancer. The use of estrogen-only or combined estrogen-progestogen HRT has been associated with a slightly increased risk of ovarian cancer. The risk of ovarian cancer varies with age. For example, in women aged 50 to 54 who are not taking HRT, about 2 women in 2000 will be diagnosed with ovarian cancer over a 5-year period. For women who have been using HRT for 5 years, there will be about 3 cases per 2000 users (i.e. about 1 extra case).
Effect of HRT on heart and circulation
Blood clots in a vein (thrombosis)
The risk of blood clots in the veins is about 1.3 to 3- times higher in HRT users than in non-users, especially during the first year of using it.
Blood clots can be serious, and if one travels to the lungs, it can cause chest pain, breathlessness, fainting or even death.
You are more likely to get a blood clot in your veins as you get older. Inform your doctor if any of these situations applies to you:
- you are unable to walk for a long time because of major surgery, injury or illness (see also section 3, If you need to have surgery)
- you are seriously overweight (BMI >30 kg/m2)
- you have any blood clotting problem that needs long-term treatment with a medicine used to prevent blood clots
- if any of your close relatives has ever had a blood clot in the leg, lung or another organ
- you have systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
- you have cancer.
Compare
Looking at women in their 50s who are not using HRT, on average, over a 5-year period, 4 to 7 in 1000 would be expected to get a blood clot in a vein.
For women in their 50s who have been using estrogen-progestogen HRT for over 5 years, there will be 9 to 12 cases in 1000 users (i.e.an extra 5 cases).
For women in their 50s who have had their womb removed and have been using estrogen-only HRT for over 5 years, there will be 5 to 8 cases in 1000 users (i.e. 1 extra case).
Heart disease (heart attack)
There is no evidence that HRT will prevent a heart attack.
Women over the age of 60 years who use estrogen-progestogen HRT are slightly more likely to develop heart disease than those not using any HRT.
For women who have had their womb removed and are using estrogen-only therapy there is no increased risk of developing a heart disease.
Stroke
The risk of getting stroke is about 1.5 times higher in HRT users than in nonusers. The number of extra cases of stroke due to use of HRT will increase with age.
Compare
Looking at women in their 50s who are not using HRT, on average, 8 in 1000 would be expected to have a stroke over a 5-year period. For women in their 50s who are using HRT, there will be 11 cases in 1000 users, over 5 years (i.e. an extra 3 cases).
Other conditions
HRT will not prevent memory loss. There is some evidence of a higher risk of memory loss in women who start using HRT after the age of 65. Speak to your doctor for advice.
Do not use this medicine if you are pregnant.
Estrogel is for use in postmenopausal women only. If you become pregnant, stop using Estrogel and contact your doctor.
Do not breastfeed if you are using this medicine.
If you have not told your doctor about any of the above, tell them before you start taking Estrogel.
Taking other medicines
Tell your pharmacist or doctor if you are taking any other medicines, including any that you get without a prescription from your pharmacy, supermarket or health food shop.
Estrogel and some other medicines may interfere with each other. These include:
- Skin cleansers and detergents e.g. products containing benzalkonium chloride or sodium lauryl sulphate.
- Other skin products containing alcohol e.g. astringents or sunscreens.
- Products to treat skin and scalp disorders e.g. products to cure warts, acne or dandruff.
- Other skin medications which change how skin is made, e.g. anti-cancer products.
- Medicines for epilepsy (such as lamotrigine, phenobarbital, phenytoin and carbamazepine).
- Medicines for tuberculosis (such as rifampicin, rifabutin).
- Medicines for HIV infection (such as nevirapine, efavirenz, ritonavir and nelfinavir).
- Herbal products containing St John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum).
HRT can affect the way some other medicines work:
- A medicine for epilepsy (lamotrigine), as this could increase frequency of seizures.
- Medicines for Hepatitis C virus (HCV) (such as combination regimen ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ ritonavir with or without dasabuvir as well as a regimen with glecaprevir/pibrentasvir) may cause increases in liver function blood test results (increase in ALT liver enzyme) in women using Combined Hormonal Contraceptives (CHCs) containing ethinylestradiol. Estrogel contains estradiol instead of ethinylestradiol. It is not known whether an increase in ALT liver enzyme can occur when using Estrogel with this HCV combination regimen.
These medicines may be affected by Estrogel or may affect how well it works. You may need different amounts of your medicines, or you may need to take different medicines.
Your doctor and pharmacist will have more information on these and other medicines to be careful with or avoid while taking this medicine.
How to use Estrogel
Follow all directions given to you by your doctor or pharmacist carefully.
They may differ from the information contained in this leaflet.
If you do not understand the instructions printed on the pharmacist label, ask your pharmacist or doctor for help.
How much to use
• Your doctor will prescribe the lowest effective dose for the shortest time to treat your symptoms.
• One pump is equal to one measure
• The usual daily dose is 2 measures (i.e. 2 pumps) of gel. The Pump pack will last four weeks.
• If 4 measures (i.e. 4 pumps) of gel have been prescribed, the Pump Pack will last two weeks.
Spread the gel on a large area of skin on each shoulder, outer arm and/or each mid-inner thigh.
How to use it
• If you have never used any other HRT medicines or you are switching to Estrogel from a period-free HRT product, you can start using Estrogel on any convenient day.
• If you are currently using another type of HRT where you have a period, finish your current medicine pack before you start using Estrogel.
• Do not ask anyone else to apply the gel. Only you should apply your medicine.
• Do not use strong skin cleaners or detergents when washing the area where you will apply the gel.
• Avoid close skin contact with your partner for one hour after application.
• Do not wash the skin or apply other skin care products until at least one hour after application.
• If the prescribed dose does not provide relief, tell your doctor. Do not use more than the prescribed dose.
Your doctor will aim to prescribe the lowest effective dose to treat your symptoms for as short as necessary. Speak to your doctor if you think this dose is too strong or not strong enough.
Preparing your new Pump Pack
Before using your new Pump Pack for the first time, you need to prepare it for use as follows:
• Remove the cap from the canister.
• Press the plunger down a few times until the gel comes out.
- Do not use this first dose of gel from your Pump Pack. This dose should be discarded.
• Your Pump Pack is now ready to use.
How much to use and when to use
• Apply the gel once a day, either in the morning or evening.
• Try to use the gel at about the same time each day.
• Your doctor will prescribe the lowest effective dose for the shortest time to treat your symptoms.
• One pump is equal to one measure.
Make sure to push the pump firmly down to ensure a full pump is delivered.
• The usual daily dose is 2 measures (i.e. 2 pumps) of gel. The Pump pack will last four weeks.
• If 4 measures (i.e. 4 pumps) of gel have been prescribed, the Pump Pack will last two weeks.
• The correct dose of gel should be dispensed and applied to clean, dry, intact areas of skin e.g. on the arms and shoulders, and/or inner thighs. The area of application should be as large as possible see table below.
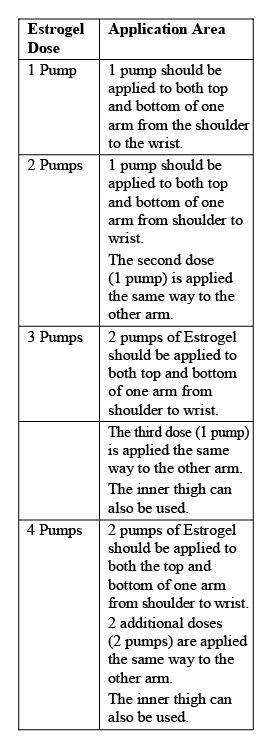
How to apply the gel
1. Make sure that your hands and the skin where you are going to apply the gel are clean, dry and unbroken.
2. Remove the canister cap to reveal the plunger.
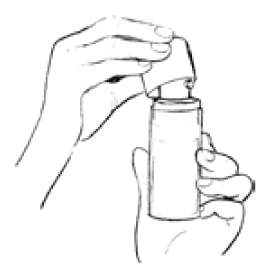
3. Hold the Estrogel Pump Pack in one hand and place your other hand under the spout, ready to collect the gel.
4. Push the plunger down firmly. This will dispense one measure of the gel.
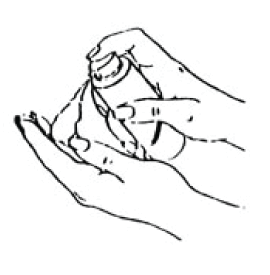
5. Apply the gel as per table above, to either:
• the outer arm and shoulder of one or both arms,
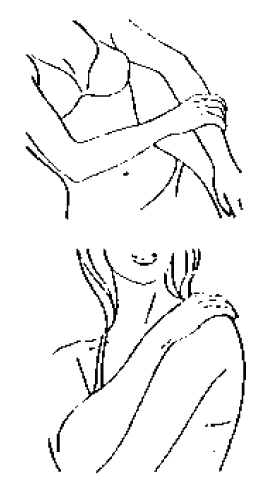
or
• the mid-inner thigh of one or both legs.
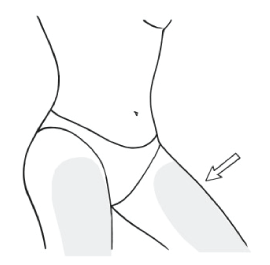
6. Do not apply on or near the breasts, or near the genital area.
7. Spread the gel over a large area of skin on each shoulder, outer arm or mid-inner thigh keeping the area of application as constant as possible from day to day.
8. If your doctor has prescribed 2 measures of gel, spread 1 measure over each outer arm and shoulder, or each mid-inner thigh. If 3 measures of gel have been prescribed, spread the gel over each arm and shoulder or each mid-inner thigh. If 4 measures of gel have been prescribed, spread 2 measures over each outer arm and shoulder or each mid-inner thigh. (See steps 4-8).
9. Replace the cap.
10. Leave to dry for 5 minutes before covering with clothes.
11. Wash hands with soap and water after applying the gel.
If you believe Estrogel has been transferred to another person (man or child):
Wash the area of skin onto which may have been affected immediately with soap and water.
How you know when your Pump Pack is empty
The Pump Pack is nearly empty when the plunger does not return back to its original position after you have pushed it down.
When this happens, do not use the Pump Pack any longer. Start using a new Pump Pack
When to take it
• Apply the gel once a day, either in the morning or evening.
• Try to use the gel at about the same time each day.
How long to take it
Your doctor will prescribe the lowest effective dose for the shortest time to treat your symptoms.
If you forget to take it
• If it is more than 12 hours until your next dose, apply the gel as soon as you remember and apply the next dose at the normal time.
• If it is less than 12 hours until your next dose, skip the missed dose and apply the next dose at the normal time.
• Do not use a double dose (two doses at the same time) to make up for a forgotten dose.
• If you forget a dose you may have breakthrough bleeding or spotting.
If you take too much (overdose)
Immediately telephone your doctor or the Poisons Information Centre (telephone 13 11 26) for advice, or go to Accident and Emergency at the nearest hospital, if you think that you or anyone else may have taken too much Estrogel.
The effects of overdosing are generally: breast tenderness, nausea and vaginal bleeding. These symptoms disappear when treatment is stopped or the dose is reduced.
While you are using Estrogel
Things you must do
Talk to your pharmacist or doctor if your symptoms do not improve.
Your pharmacist or doctor will assess your condition and decide if you should continue to take the medicine.
The use of HRT carries risks which need to be considered when deciding whether to start using it, or whether to carry on using it.
The experience in treating women with a premature menopause (due to ovarian failure or surgery) is limited. If you have a premature menopause the risks of using HRT may be different. Please talk to your doctor.
Before you start (or restart) HRT your doctor will ask you about your own and your family’s medical history. Your doctor may decide to perform a physical examination. This may include an examination of your breasts and/or an internal examination, if necessary.
Once you have started on Estrogel you should see your doctor for regular check-ups (at least once a year). At these check-ups, discuss with your doctor the benefits and risks of continuing with Estrogel.
Go for regular breast screening, as recommended by your doctor.
If you need to have surgery
If you are going to have surgery, tell the surgeon that you are using Estrogel. You may need to stop using Estrogel about 4 to 6 weeks before the operation to reduce the risk of a blood clot. Ask your doctor when you can start using Estrogel again.
Things you must not do
Do not give your medicine to anyone else, even if they have the same condition as you.
Do not stop using your medicine or change the dosage without checking with your doctor.
Side effects
Tell your pharmacist or doctor as soon as possible if you do not feel well while you are taking Estrogel.
All medicines can have side effects. Sometimes they are serious, most of the time they are not. You may need medical attention if you get some of the side effects.
Do not be alarmed by the following lists of side effects. You may not experience any of them.
Ask your pharmacist or doctor to answer any questions you may have.
Tell your pharmacist or doctor if you notice any of the following and they worry you:
- Headache.
- Nausea, abdominal pain.
- Breast swelling or pain, breast enlargement, menstrual cramps, heavy menstrual bleeding, vaginal discharge.
- Weight change (increase or decrease), water retention with peripheral oedema.
- Depression, mood swings.
- Vertigo.
- Flatulence, vomiting.
- Benign breast or uterine tumour,
- Increased volume of uterine leiomyoma,
- Vaginitis or vaginal candidiasis.
- Feeling weak (asthenia).
- Glucose intolerance.
- Change in libido.
- Hypertension.
- Skin decolouration, acne.
- Appearance of milk secretion (galactorrhea).
The above list includes the more common side effects of your medicine. They are usually mild.
If any of the following happen, tell your doctor immediately or go to Accident and Emergency at your nearest hospital:
- shortness of breath
- wheezing or difficulty breathing
- swelling of the face, lips, tongue or other parts of the body
- rash, itching or hives on the skin
- Sudden chest pain
- Pain in your chest that spreads to your arm or neck
- Yellowing of the eyes and face, darkening of urine, itchy skin (jaundice)
- Unexpected vaginal bleeding or spotting (breakthrough bleeding) after using Estrogel for some time, or after you stop treatment
- Breast change, including dimpling of the breast skin, change in the nipple, lumps that you can see or feel (breast cancer)
- Painful menstrual periods
- Unexplained migraine-like headaches
- Rash with target-shaped reddening or sores (erythema multiforme)
- Anaphylactic reaction (in women with past history of allergic reaction)
The above list includes very serious side effects. You may need urgent medical attention or hospitalisation.
Tell your pharmacist or doctor if you notice anything that is making you feel unwell.
Other side effects not listed above may also occur in some people.
After using Estrogel
Storage
Keep your medicine in the original pack until it is time to use it.
Keep your medicine in a cool dry place where the temperature stays below 30°C.
Do not store Estrogel or any other medicine in the bathroom or near a sink. Do not leave it on a window sill or in the car.
Heat and dampness can destroy some medicines.
Keep it where children cannot reach it.
A locked cupboard at least one-and-a-half metres above the ground is a good place to store medicines.
Disposal
Ask your pharmacist what to do with any medicine that is left over, or if the expiry date has passed.
Product description
What it looks like
Estrogel is a non-greasy, non-staining, clear, colourless, transdermal gel with an odour of alcohol.
Estrogel is a gel for transdermal use provided in a 80g bottle with a metered dose pump. Each Pump Pack delivers 64 metered doses.
Ingredients
The active ingredient is estradiol hemihydrate. This is a manmade form of the female hormone estrogen.
Each 1.25g dose of Estrogel gel contains 0.75 mg of estradiol (as hemihydrate).
It also contains:
- Carbomer 980, trolamine, ethanol and purified water.
This medicine does not contain lactose, sucrose, gluten, tartrazine or any other azo dyes.
Supplier
Estrogel is supplied in Australia by:
Besins Healthcare Australia Pty Ltd
Level 16, Tower 2, Darling Park,
201 Sussex Street,
Sydney, NSW 2000
® = Registered Trademark
Australian Registration Number
AUST R 301620
This leaflet was prepared in August 2023
