What is in this leaflet
This leaflet answers some common questions about Fentora. It does not contain all of the available information. It does not take the place of talking to your doctor or pharmacist.
All medicines have risks and benefits. Your doctor has weighed the risks of your taking Fentora against the benefits they expect it will have for you.
If you have any concerns about taking Fentora, talk to your doctor or pharmacist.
Keep this leaflet with the medicine. You may want to read it again.
What Fentora is used for
Fentora contains a medicine called fentanyl citrate. It is a pain-relieving medicine known as an opioid, which is used to treat breakthrough pain in adult patients with cancer who are already taking other opioid pain medicines for their persistent (around-the-clock) cancer pain.
Breakthrough pain is additional sudden pain that occurs in spite of you having taken your usual opioid pain-relieving medicines.
Opioid medicines are those that contain active ingredients such as morphine, fentanyl citrate, codeine, methadone, oxycodone, pethidine or buprenorphine.
Ask your doctor if you have any questions about why Fentora orally disintegrating tablets have been prescribed for you. Your doctor may have prescribed it for another use.
Fentora is only available on a doctor's prescription.
Before you take it
Fentora is not suitable for everyone.
When you must not take it
Do not take Fentora if:
- you suffer from short-term pain or chronic pain other than breakthrough pain, such as pain from injuries or surgery, headaches or migraines.
- you have not been prescribed opioid pain medicine ever.
- you have not been prescribed opioid pain medicine every day on a regular schedule, for at least one week, to control your persistent pain. If you have not been using these medicines you must not use Fentora, because it may increase the risk that breathing could become dangerously slow and/or shallow, or even stop.
- you are allergic (hypersensitive) to fentanyl, or any of the other ingredients of Fentora (see list at the end of this leaflet).
- you suffer from severe breathing problems or severe obstructive lung conditions
- you are also taking, or used in the last 2 weeks, medicines referred to as Monoamine Oxidase (MAO) Inhibitors.
Do not take Fentora after the expiry date shown on the blister package label and the carton.
Do not take Fentora if the packaging seems to have been opened or is damaged.
Things to be careful of
Addiction
You can become addicted to Fentora even if you take it exactly as prescribed. Fentora may become habit forming causing mental and physical dependence. If abused it may become less able to reduce pain.
Dependence
As with all other opioid containing products, your body may become used to you taking Fentora. Taking it may result in physical dependence. Physical dependence means that you may experience withdrawal symptoms if you stop taking Fentora suddenly, so it is important to take it exactly as directed by your doctor.
Tolerance
Tolerance to Fentora may develop, which means that the effect of the medicine may decrease. If this happens, more may be needed to maintain the same effect.
Continue taking your medicine for as long as your doctor tells you. If you stop having this medicine suddenly, your pain may worsen and you may experience some or all of the following withdrawal symptoms:
- nervousness, restlessness, agitation, trouble sleeping or anxiety
- body aches, weakness or stomach cramps
- loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting or diarrhoea
- increased heart rate, breathing rate or pupil size
- watery eyes, runny nose, chills or yawning
- increased sweating.
DO NOT use Fentora during labour and delivery.
It is important that you do not exceed your recommended dose.
Before you start to take it
Tell your doctor if:
- you have any allergies
- you are pregnant or intend to become pregnant
- you are breast feeding or planning to breast feed
- your other opioid pain medicine you take for your persistent (around-the-clock) cancer pain is not stabilized yet
- you are suffering from any condition that has an effect on your breathing (such as asthma, wheezing, or shortness of breath).
- You have a head injury
- You have exceptionally slow heart rate or other heart problems
- You have liver or kidney problems, as these organs have an effect on the way in which your system breaks down the medicine.
- You have low amount of fluid in the circulation or low blood pressure
- You have a history of addiction or substance abuse either personally or within your family
- You experience an unexplained increase in pain.
- You feel anxious, irritable or have sudden mood swings, these could be signs of addiction
- You notice any changes in hormones such as prolactin, testosterone and cortisol from blood tests.
Your doctor should monitor you for these signs while on treatment. They may also conduct blood tests from time to time to ensure you are responding as expected to treatment.
These organs have an effect on the way in which your system breaks down the medicine.
Taking other medicines
Tell your doctor if you are taking any other medicines, including any that you buy without a prescription from your pharmacy, supermarket or health food store.
Take special care with Fentora if:
- you are taking any medicines which might normally have a sedative effect (make you sleepy), such as:
- sleeping pills
- medicines to treat anxiety
- antihistamines
- tranquillisers. - Other strong analgesics used to manage pain such as morphine, codeine, methadone, oxycodone, pethidine or buprenorphine.
- you are taking any medicines or other substances that might have an effect on the way in which your body breaks down Fentora, such as:
- medicines used to treat fungal infections, such as ketoconazole, itraconazole, and fluconazole
- medicines that help control HIV infection, such as ritonavir, nelfinavir, amprenavir, and fosamprenavir
- certain antibiotics such as clarithromycin and erythromycin
- medicines used for severe nausea
- medicines used to treat high blood pressure or heart disease, such as diltiazem and verapamil
- medicines used for severe depression known as selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or serotonin norepinephrine re-uptake inhibitors (SNRIs) or have done so in the past 2 weeks
- muscle relaxants (such as cyclobenzaprine, metaxalone)
- medicines used for severe depression called monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) or have done so in the past 2 weeks
Using FENTORA with food or drink
- Fentora may be used before or after, but not during, meals. You may drink some water before using Fentora to help moisten your mouth, but you should not drink or eat anything while taking the medicine.
- You should not drink grapefruit juice while using Fentora because it may affect the way your body breaks down Fentora
- Do not drink alcohol while using Fentora. It can increase the risk of experiencing dangerous side effects
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking any medicine.
Fentora should not be used during pregnancy or breastfeeding. Breastfeeding should not be restarted until at least 6 days after the last administration of Fentora, unless you have discussed this with you doctor.
Driving and using machines
- You should discuss with your doctor whether it is safe for you to drive, or operate machinery after taking Fentora.
Do not drive or operate machinery if you: are feeling sleepy or dizzy; have blurred or double vision; or have difficulty in concentrating. It is important you know how you react to Fentora before driving or operating machinery.
Important information about some of the ingredients of Fentora
Each tablet of Fentora 100 micrograms contains 10 mg of sodium. Each tablet of Fentora 200 micrograms, Fentora 400 micrograms, Fentora 600 micrograms and Fentora 800 micrograms contains 20 mg of sodium. You should take this into consideration and seek advice from your doctor.
How to take it
Do not take Fentora to treat any condition other than that directed by your doctor.
Fentora orally disintegrating tablets are for buccal use. When you place a tablet in your mouth, it dissolves and the medicine is absorbed through the lining of your mouth, into the blood system. Taking the medicine in this way allows it to be absorbed quickly to relieve your breakthrough pain.
How many to take
When you first start Fentora, your doctor will work with you to find the dose that will relieve your breakthrough pain. This process is called the titration process. Please refer to the titration flowchart in the Patient's guide for Fentora section of the leaflet for more information.
It is very important that you use Fentora exactly as the doctor tells you.
The initial dose is 100 micrograms. During determination of your right dose, your doctor may instruct you to take more than one tablet per episode. If your breakthrough pain is not relieved after 30 minutes, use only 1 more tablet of Fentora during the titration period.
Ask your doctor if you are not sure about the right dose or if you have any questions about taking Fentora.
You should start to feel some pain relief quickly while you are taking Fentora.
Contact your doctor if your right dose of Fentora does not relieve your breakthrough pain. Your doctor will decide if your dose needs to be changed.
It is recommended that you wait at least 4 hours before treating another episode of breakthrough pain with Fentora. The frequency may be increased if instructed by your doctor.
You must tell your doctor immediately if you are using Fentora more than four times per day, as the doctor may wish to change your medicine for your persistent pain. Once your persistent pain has been controlled, your doctor may need to change your dose of Fentora further.
For the most effective relief, let your doctor know about your pain and how Fentora is working for you so that the dose can be changed if needed.
Do not change doses of Fentora or your other pain medicines on your own. Any change in dosage must be prescribed and monitored by your doctor.
If you are not sure about the right dose, or if you have questions about taking this medicine, you should contact your doctor.
DO NOT TAKE MORE THAN THE DOSE YOUR DOCTOR HAS RECOMMENDED. Change in dosage must be directed and monitored by your doctor.
How to take it
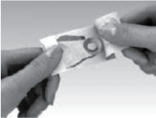
- Open the blister only when you are ready to use the tablet.
The tablet must be used immediately once removed from the blister.
Separate one of the blister units from the blister card by tearing apart at the perforations.
Bend the blister unit along the line where indicated.
Peel the blister backing to expose the tablet. Do NOT attempt to push the tablet through the blister, because this can damage the tablet.
Remove the tablet from the blister unit and immediately place the entire tablet near a molar tooth between the gum and the cheek (as shown in the picture).
Do not attempt to crush or split the tablet.
Sometimes your doctor may tell you to place the tablet under your tongue instead.

Do not bite, suck, chew, or swallow the tablet, as this will result in less pain relief than when taken as directed.
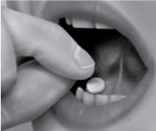
- The tablet should be left between the cheek and gum until dissolved, which usually takes approximately 14 to 25 minutes.
- You may feel a gentle bubbling sensation between your cheek and gum as the tablet dissolves.
- In case of irritation, you may change the placement of the tablet on the gum.
- After 30 minutes, if pieces of the tablet remain, they may be swallowed with a glass of water.
Always write the date and time each time you take Fentora tablet. A table called the 'Titration Dose Record' and 'Maintenance Dosing Record' in the leaflet located inside the box will help you record this information.
This will help you and your doctors monitor your pain level and if the dose is right for you.
Fentora contains no added flavours. You may sense a slight taste, or you may notice nothing at all.
How long to take it
You should not normally stop taking Fentora for breakthrough pain unless your doctor tells you to.
If you are taking high doses of Fentora and feel that the pain is getting worse with time please speak to your doctor.
Tell your doctor if you feel unwell during your course of treatment.
If you take too many Fentora units (overdose)
If you or someone else receive too much (overdose), and experience one or more of the symptoms below, immediately call triple zero (000) for an ambulance. Keep the person awake by talking to them or gently shaking them every now and then. You should follow the above steps even if someone other than you has accidentally used Fentora that was prescribed for you. If someone takes an overdose they may experience one or more of the following symptoms:
- Slow, unusual or difficult breathing
- Drowsiness, dizziness or unconsciousness
- Slow or weak heartbeat
- Nausea or vomiting
- Convulsions or fits
If you think you or someone else may have used too much Fentora, you should immediately:
- telephone your doctor, or
- the Poisons Information Centre (telephone 13 11 26) or
- go to Accident and Emergency at your nearest hospital
Do this even if there are no signs of discomfort or poisoning.
When seeking medical attention, take this leaflet and remaining medicine with you to show the doctor. Also tell them about any other medicines or alcohol which have been taken.
The most common side effects are feeling sleepy, sick or dizzy. If you begin to feel very dizzy, or very sleepy before the tablet is completely dissolved, rinse your mouth with water and spit the remaining pieces of the tablet into a sink or toilet right away. Call another person to help you.
A serious side effect of Fentora is slow and/or shallow breathing. This can occur if your dose of this medicine is too high or if you take too much Fentora. You and your carer should discuss this side effect with your doctor immediately.
What to do if a child or adult accidentally takes Fentora
If you think someone has accidentally taken Fentora follow these steps:
- If the person is asleep, wake them up by calling their name and shaking their arm or shoulder.
- CALL FOR EMERGENCY HELP.
- While waiting for emergency help:
- if the person seems to be breathing slowly, prompt them to breathe every 5-10 seconds
- if the person has stopped breathing give mouth to mouth resuscitation until help arrives.
While you are taking it
Things you must do
Make sure that all of your doctors and pharmacists know about your use of Fentora. Remind them if any new medicines are about to be started, including any medicines that you may purchase without a prescription.
Things that you must not do
Do not use Fentora to treat any other complaints unless your doctor tells you to. It may not be safe to use Fentora for another complaint.
Do not give Fentora to someone else even if their symptoms are the same. Fentora should only be used by the person for whom it was prescribed. It may not be safe for another person to use Fentora.
Do not stop using Fentora unless your doctor advises you to do so. If you have been using Fentora for a long period of time but stop using it suddenly without your doctor's advice, you may experience withdrawal symptoms (such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, anxiety and shivering). Seek your doctor's advice if you experience these symptoms.
If you become pregnant whilst taking Fentora, you should stop taking it and see your doctor immediately.
Side Effects
All medicines can have side effects. Sometimes they are serious, most of the time they are not. You may need medical treatment if you get some side effects. Do not be alarmed by this list of possible side effects. You may not experience any of them.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist to answer any questions you may have.
Tell your doctor if you experience any of the following:
- headache
- nausea/vomiting
- feeling unwell
- weakness, dizziness
- sleepiness, sedation
- constipation
- anxiety.
If you feel excessively dizzy, sleepy or otherwise ill while taking Fentora, remove the Fentora unit and contact your doctor for further directions on using Fentora.
Tell your doctor immediately, or get someone to take you to Accident and Emergency at your nearest hospital if you notice any of the following:
- becoming very sleepy
- having slow or shallow breathing
- sudden signs of allergy such as rash, itching or hives on the skin, swelling of the lips, tongue or throat, shortness of breath, wheezing or trouble breathing.
Opioids can cause sleep-related breathing disorders including central sleep apnoea (CSA) and sleep-related hypoxemia (insufficient oxygen intake).
Make sure that you are with someone who can keep you awake by talking to you or gently shaking you every now and then.
Whilst using the Fentora tablet you may experience irritation, pain, gum bleeding or an ulcer at the site of application.
Tell your doctor if you notice anything else that is making you feel unwell. Other side effects not listed in this leaflet may also occur in some patients.
After using it
Storage
Keep Fentora in the original package until it is time to take the dose. If you take Fentora out of its blister package, it may not keep as well.
Do not use it if the blister package has been damaged or opened before you are ready to use it.
Keep Fentora in a cool dry place where the temperature stays below 25°C.
Do not store it or any other medicine in the bathroom or near a sink. Do not leave it in the car on hot or cold days. Heat, cold and dampness can destroy some medicines.
Fentora orally disintegrating tablets must be kept out of the reach of children. The pain-relieving medicine in Fentora is very strong and could be life-threatening if taken accidentally by a child.
A locked cupboard at least one- and-a-half metres above the ground is a good place to store medicines.
Disposal
If you no longer need to use this medicine or it is out of date, take it to any pharmacy for safe disposal.
Product description
What Fentora looks like
The orally disintegrating tablets are flat-faced, round, bevelled-edge tablets, embossed one side with a "C" and on the other side with "1" for FENTORA 100 micrograms, with "2" for FENTORA 200 micrograms, with "4" for FENTORA 400 micrograms, with "6" for FENTORA 600 micrograms, with "8" for FENTORA 800 micrograms.
FENTORA is supplied in individually sealed, child-resistant blister packs.
Ingredients
Active ingredient:
The active ingredient is fentanyl, present in the product as fentanyl citrate.
Inactive ingredients:
- mannitol
- sodium starch glycollate type A
- sodium hydrogen carbonate
- sodium carbonate
- citric acid
- magnesium stearate
Manufacturer/Supplier
Fentora is manufactured in the USA.
Supplied in Australia by:
Teva Pharma Australia Pty Ltd
Level 1, 37 Epping Rd
Macquarie Park
NSW 2113
Telephone: 1800 288 382
Australian Registration Numbers:
Fentora 100 micrograms:
AUST R 218435
Fentora 200 micrograms:
AUST R 218437
Fentora 400 micrograms:
AUST R 218433
Fentora 600 micrograms:
AUST R 218434
Fentora 800 micrograms:
AUST R 218436
Fentora is a registered trademark of Cima Labs Inc.
This leaflet was prepared in August 2021.
Published by MIMS October 2021

