Boxed Warnings
Life threatening lactic acidosis can occur due to accumulation of metformin. Risk factors include renal impairment, old age and the use of high doses of metformin above 2 g per day.
1 Name of Medicine
Metformin hydrochloride.
2 Qualitative and Quantitative Composition
Formet tablets come in four strengths:
Formet 250 contains 250 mg metformin hydrochloride.
Formet 500 contains 500 mg metformin hydrochloride.
Formet 850 contains 850 mg metformin hydrochloride.
Formet 1000 contains 1000 mg metformin hydrochloride.
The tablets are gluten free.
For the full list of excipients, see Section 6.1 List of Excipients.
3 Pharmaceutical Form
Film-coated tablets.
Formet 250. Round, white tablet (approx. 9 mm), embossed with MO on one side and the Arrow symbol, ">" on the other.
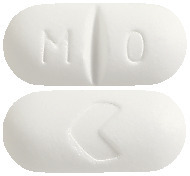
Formet 500. Oblong, white film-coated tablet, embossed with M/O on one side and the Arrow symbol, ">" on the other.
Formet 850. Round, white film-coated tablet (approx. 13 mm), embossed with MO on one side and the Arrow symbol, ">" on the other.
Formet 1000. Oval, white tablet, embossed with M/O on one side and ">/>" on the other.
4 Clinical Particulars
4.9 Overdose
Symptoms. Hypoglycaemia has not been seen with ingestion of up to 85 g of metformin alone, although lactic acidosis has occurred in such circumstances. The onset of lactic acidosis is often subtle and accompanied only by nonspecific symptoms such as malaise, myalgia, respiratory distress, increasing somnolence and nonspecific abdominal distress. There may be associated hypothermia, hypotension and resistant bradyarrhythmias with more marked acidosis. Lactic acidosis should be suspected in any diabetic patient with metabolic acidosis lacking evidence of ketoacidosis (ketonuria and ketonaemia).
Treatment. Lactic acidosis should be feared in diabetic metformin treated patients with overdose. Lactic acidosis is diagnosed and monitored by measurement of serum electrolytes, arterial pH and pCO2 and arterial lactate plasma level.
The aim of treatment is to manage any underlying disorder and in some cases this will be sufficient to enable the body's homeostatic mechanism to correct the acid-base imbalance. The advantages of more active treatment of the acidosis must be balanced against the risks, including over alkalinisation with sodium bicarbonate. Because metformin hydrochloride is dialysable (with a clearance of up to 170 mL/min under good haemodynamic conditions), prompt haemodialysis is recommended to correct the acidosis and remove the accumulated metformin.
For information on the management of overdose, contact the Poisons Information Centre on 13 11 26 (Australia).
5 Pharmacological Properties
5.3 Preclinical Safety Data
Genotoxicity. No evidence of a mutagenic potential of metformin was found in the Ames test (S. typhimurium), gene mutation test (mouse lymphoma cells), chromosomal aberrations test (human lymphocytes), or in vivo micronuclei test (mouse bone marrow).
Carcinogenicity. Long term carcinogenicity studies have been performed in rats (dosing duration of 104 weeks) and mice (dosing duration of 91 weeks) at doses up to and including 900 mg/kg/day and 1500 mg/kg/day, respectively. These doses are both approximately two to three times the recommended human daily dose on a body surface area basis. No evidence of carcinogenicity with metformin was found in either male or female mice. Similarly, there was no tumourigenic potential observed with metformin in male rats. However, an increased incidence of benign stromal uterine polyps was seen in female rats treated with 900 mg/kg/day.
6 Pharmaceutical Particulars
6.7 Physicochemical Properties
Chemical structure. The chemical name for metformin hydrochloride is 1,1 dimethyl biguanide hydrochloride. Its structural formula is:
https://stagingapi.mims.com/au/public/v2/images/fullchemgif/CSMETFOH.gif C4H11N5.HCl. Molecular weight: 165.6.
Metformin hydrochloride is a white, crystalline powder which is odourless or almost odourless and hygroscopic. It is freely soluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol (96%), and practically insoluble in chloroform and ether.
CAS number. 1115-70-4.
7 Medicine Schedule (Poisons Standard)
S4 - Prescription Only Medicine.
Summary Table of Changes
https://stagingapi.mims.com/au/public/v2/images/fulltablegif/FORTABST.gif