What is in this leaflet
This leaflet answers some common questions about FOSAMAX PLUS. It is particularly important that you read the sections "When to take it" and "How to take it" before you take this medicine. This leaflet does not contain all the available information.
It does not take the place of talking to your doctor or pharmacist.
All medicines have risks and benefits. Your doctor has weighed the risks of you taking FOSAMAX PLUS against the benefits they expect it will have for you.
If you have any concerns about taking this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Keep this leaflet with the medicine. You may need to read it again.
What FOSAMAX PLUS is used for
FOSAMAX PLUS is used to treat osteoporosis and to provide additional vitamin D.
Osteoporosis is caused by changes in the way bone is normally maintained. Vitamin D is an essential nutrient required for calcium absorption and healthy bones.
Understanding bone
Bone is a living, growing tissue. Throughout life, our bodies are breaking down old bone and rebuilding new bone in a continuous cycle. Until our late 20s, while bones are still developing, we gain bone by building more than we lose. From then until about age 35 the process is usually in balance, so that the amount of bone lost is about equal to the amount that is replaced. This balanced process keeps your skeleton healthy and strong. After about age 35 this balance is disturbed, with bone loss occurring at a slightly faster rate than it can be replaced. In women, after menopause, hormonal changes cause bone loss at an even faster rate. When bone loss is excessive, bones can become thinner and weaker, and therefore are more likely to break.
Osteoporosis
"Osteo" means bone, and "porosis" means something that has holes in it, like a sponge. Therefore, osteoporosis is a disease which causes bones to become more porous, gradually making them weaker, more brittle and likely to break.
Osteoporosis is common in postmenopausal women. The menopause occurs when the ovaries virtually stop producing the female hormone, oestrogen, or are removed (which may occur, for example, at the time of a hysterectomy). At this time, bone is removed faster than it is formed, so bone loss occurs and bones become weaker. The earlier a woman reaches the menopause, the greater the risk of osteoporosis.
Osteoporosis also occurs in men but is less common than in women.
Early on, osteoporosis usually has no symptoms. However, if left untreated it can result in broken bones, also called fractures. Although fractures usually cause pain, fractures of the bones of the spine may go unnoticed until they cause height loss. Fractures may occur during normal, everyday activity, such as lifting, or from minor injury that would not ordinarily fracture normal bone. Fractures usually occur at the hip, spine, or wrist and can lead not only to pain, but also to considerable deformity and disability, such as stooped posture from curvature of the spine, and loss of mobility.
What should I know about vitamin D?
Vitamin D is an essential nutrient, required for calcium absorption and healthy bones. The main source is through exposure to summer sunlight, which makes vitamin D in our skin. Clothing or sun block can prevent enough sunlight from getting through. In addition, as people age, their skin becomes less able to make vitamin D. Very few foods are natural sources of vitamin D.
Too little vitamin D leads to inadequate calcium absorption and low phosphate-minerals that make bones strong. Even if you are eating a diet rich in calcium or taking a calcium supplement, your body cannot absorb calcium properly unless you have enough vitamin D. Too little vitamin D may lead to bone loss and osteoporosis. Severe vitamin D deficiency may cause muscle weakness which can lead to falls and a higher risk of fracture.
How does FOSAMAX PLUS work?
The alendronate in FOSAMAX PLUS works by slowing down the process of old bone being removed, which allows the bone-forming cells time to rebuild normal bone. Alendronate not only helps prevent the loss of bone but actually helps to rebuild bone and make bone less likely to fracture. Thus, FOSAMAX PLUS reverses the progression of osteoporosis.
FOSAMAX PLUS starts working on the bone cells immediately, but measurable effects on bone mass may not be seen for several months or more.
The alendronate in FOSAMAX PLUS belongs to a group of non-hormonal medicines called bisphosphonates.
In addition to alendronate, FOSAMAX PLUS also contains vitamin D, an essential nutrient required for calcium absorption and healthy bones.
Before you take FOSAMAX PLUS
You should know that in some people, FOSAMAX PLUS can irritate or burn the food pipe (also called oesophagus). The chances of this happening should be reduced when you follow the instructions for 'How to take FOSAMAX PLUS' in this leaflet.
When you must not take it
Do not take FOSAMAX PLUS if:
- you have an allergy to FOSAMAX PLUS or any of the ingredients listed at the end of this leaflet
- you have certain disorders of the food pipe (oesophagus) including those that cause difficulty in swallowing
- you are unable to stand or sit upright for at least 30 minutes
- your doctor has told you that you currently have low blood calcium
- your dentist advises you to consult your doctor first
Do not take FOSAMAX PLUS if you are pregnant or breast-feeding. FOSAMAX Plus has not been studied in pregnant or breast-feeding women.
Do not take FOSAMAX PLUS if:
- the packaging is torn or shows signs of tampering
-
the expiry date on the pack has passed.
If you take this medicine after the expiry date has passed, it may not work.
If you are not sure whether you should start taking FOSAMAX PLUS, talk to your doctor.
Do not give FOSAMAX PLUS to a child. FOSAMAX PLUS has not been studied in children.
Before you start to take it
Tell your doctor if:
- you plan to become pregnant or breast-feed
- you have any medical conditions, especially the following:
- kidney disease
- swallowing or digestive problems, such as ulcers
- you have any allergies to any other medicines or any other substances, such as foods, preservatives or dyes
- you have dental or jaw-bone problems or are planning to have a course of dental surgery.
- you currently smoke or have been a smoker in the past.
If you have not told your doctor about any of the above, tell them before you take any FOSAMAX PLUS.
Taking other medicines
Tell your doctor if you are taking any other medicines, including medicines that you buy without a prescription from your pharmacy, supermarket or health food shop. Some medicines may affect the way other medicines work.
Some medicines are likely to interfere with the absorption of FOSAMAX PLUS if taken at the same time. These include:
- antacids, medicines used to treat indigestion e.g. Gaviscon, Mylanta
- calcium supplements
- vitamins
Therefore, take FOSAMAX PLUS at least 30 minutes before taking any of these or other medicines to make sure there is no problem with absorption. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure whether you are taking any of these medicines.
You can take aspirin while you are being treated with FOSAMAX PLUS. However, both aspirin and FOSAMAX PLUS may increase the chance of stomach upsets.
Your doctor or pharmacist has more information on medicines to be careful with or avoid while taking FOSAMAX PLUS.
How to take FOSAMAX PLUS
How much to take
Take FOSAMAX PLUS only when prescribed by your doctor.
The usual dose of FOSAMAX PLUS is one tablet once a week.
Choose the day of the week that best fits your schedule. Every week, take one tablet of FOSAMAX PLUS on your chosen day.
Follow all directions given to you by your doctor carefully. They may differ from the information contained in this leaflet.
If you do not understand the instructions on the box, ask your doctor or pharmacist for help.
When and how to take it
Take FOSAMAX PLUS after getting up for the day and before taking your first food, beverage or other medication. Do not take it at bedtime.
Swallow one tablet whole with a full glass of plain water [not mineral water, not coffee or tea, not juice].
Do not take any food, medicines or drinks other than plain tap water with your FOSAMAX PLUS. It is important to take FOSAMAX PLUS with plain water only, not mineral water. Food, other drugs and mineral water and other drinks, including fruit juices, coffee and tea, will reduce the effect of FOSAMAX PLUS by interfering with the absorption into the body.
Stay upright for at least 30 minutes after swallowing FOSAMAX PLUS and do not take any food, medicines or drinks other than plain tap water during this time.
Do not lie down immediately after swallowing it. It is important to stay upright (sitting, standing or walking around) for at least 30 minutes after swallowing your tablet.
It is also very important to stay upright until after you have eaten your first food of the day. These actions will help make sure your tablet reaches your stomach quickly and help reduce the potential for irritation to your food pipe (oesophagus).
FOSAMAX PLUS is effective only if taken when your stomach is empty. Food, drinks other than plain water, and other medicines will lessen the effect of FOSAMAX PLUS by interfering with its absorption into the body.
Do not chew or suck on a tablet of FOSAMAX PLUS. Mouth ulcers may occur if the tablet is chewed or dissolved in the mouth.
How long to take it
It is important that you take FOSAMAX PLUS for as long as your doctor prescribes it. FOSAMAX PLUS can only treat your osteoporosis, by helping prevent further loss of bone and continuing to rebuild bone, if you take it every week. Since it is not known how long you should take FOSAMAX PLUS, you should discuss the need to stay on this medication with your doctor periodically to determine if FOSAMAX PLUS is still right for you.
If you forget to take it
If you miss a tablet, take one tablet on the morning after you remember.
Do not take two tablets on the same day. Return to taking one tablet once a week, as originally scheduled on your chosen day.
If you are not sure about what to do, talk to your doctor or pharmacist.
If you have trouble remembering to take your FOSAMAX PLUS, ask your pharmacist for some hints.
If you take too much (overdose)
Immediately telephone your doctor or Poisons Information Centre (telephone 13 11 26), or go to accident and emergency at your nearest hospital, if you think that you or anyone else may have taken too much FOSAMAX PLUS. Do this even if there are no signs of discomfort or poisoning.
If you take too many tablets at one time, drink a full glass of milk. Do not induce vomiting. Do not lie down.
While you are using FOSAMAX PLUS
Things you must do
If you develop difficulty or pain upon swallowing, chest pain, or new or worsening heartburn, stop taking FOSAMAX PLUS and call your doctor.
If you become pregnant while taking FOSAMAX PLUS, stop taking the tablets and tell your doctor.
If you are about to be started on any new medicine, tell your doctor and pharmacist that you are taking FOSAMAX PLUS.
If you develop a toothache or require a dental procedure, tell your dentist that you are taking FOSAMAX PLUS.
If you develop new or unusual pain in your hip, leg or other bone, tell your doctor. Rarely, patients have experienced fracture in a specific part of the thigh bone. Patients have experienced fractures in other bones as well.
Make sure you have an adequate intake of calcium in your diet. Your doctor, dietician or pharmacist can tell you what foods you should eat.
Things you must not do
Do not give FOSAMAX PLUS to anyone else, even if they have the same condition as you.
Things to be careful of
There have been side effects reported with FOSAMAX PLUS that may affect your ability to drive or operate machinery. Individual responses to FOSAMAX PLUS may vary (see Side Effects).
Things that would be helpful for your osteoporosis
Some self help measures suggested below may help your osteoporosis. Talk to your doctor or pharmacist about these measures and for more information.
- Exercise - can be helpful in building and maintaining strong bones. Regular exercise such as a brisk walk is a good idea. Talk to your doctor before you begin any exercise program.
- Diet - eat a balanced diet. You may need to increase the amount of calcium in your diet by eating calcium-rich foods or taking a calcium supplement. Your doctor will advise you.
- Smoking - appears to increase the rate at which you lose bone and, therefore, may increase your risk of fracture. Your doctor may ask you to stop smoking or at least cut down.
- Alcohol - your doctor may advise you to cut down the amount of alcohol you drink. If you drink excessively on a regular basis, you may increase your risk of developing osteoporosis.
Side Effects
Tell your doctor or pharmacist as soon as possible if you do not feel well while you are taking FOSAMAX PLUS.
FOSAMAX PLUS helps most people with osteoporosis, but it may have unwanted side effects in a few people. All medicines can have side effects. Sometimes they are serious, most of the time they are not. You may need medical treatment if you get some of the side effects.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist to answer any questions you may have.
Tell your doctor if you notice any of the following and they worry you:
- stomach pain, gas in the stomach or bowel, wind
- an uncomfortable feeling in the stomach or belching after eating, also called dyspepsia, or heartburn
- feeling sick (nausea), vomiting
- constipation, diarrhoea
- headache
- aching muscles, joints and/or bones, which rarely can be severe.
- flu-like symptoms typically at the start of treatment, such as aching muscles, generally feeling unwell and rarely fever.
- swelling of joints
- dizziness or spinning sensation
- unusual tiredness or weakness
- swelling of hands, ankles or feet
- hair loss
- changed sense of taste
Most of these are the more common side effects of FOSAMAX PLUS. For the most part, these have been mild.
Tell your doctor immediately if you notice any of the following:
- skin rash or redness of the skin, sometimes made worse by sunlight, itchiness
- mouth ulcers
- blurred vision, pain or redness in the eye
- ear pain
- symptoms of low blood calcium levels including muscle cramps or spasms or tingling sensation in the fingers or around the mouth
- new or unusual pain in your hip or thigh
These side effects are rare, and very rarely, may be serious.
Tell your dentist and doctor immediately if you notice any of the following
- Jaw-bone or dental problems (including toothache). Jaw-bone problems may include infection, and delayed healing after a tooth extraction or other work that involves drilling into the jaw-bone.
These side effects are rare and may be serious.
If any of the following happen, stop taking FOSAMAX PLUS and tell your doctor immediately:
- difficulty or pain upon swallowing
- chest pain
- new or worsening heartburn
These side effects may be due to irritation or ulceration of the food pipe. They may worsen if you continue taking the tablets. Rarely, these side effects may be serious.
If any of the following happen, stop taking FOSAMAX PLUS and tell your doctor immediately or go to accident and emergency at your nearest hospital:
- swelling of the face, lips, mouth, throat or tongue which may cause difficulty in breathing or swallowing
- pinkish, itchy swellings on the skin, also called hives or nettlerash
- severe skin reactions
- black tar-like and/or bloody stools
These may be serious side effects. You may need urgent medical attention. These side effects are rare.
If you have the swelling described above, you may be having a serious allergic reaction to FOSAMAX PLUS.
Rarely, stomach or duodenal ulcers (some severe) have occurred, but it is not known whether these were caused by FOSAMAX PLUS.
Other side effects not listed above may also occur in some patients. Tell your doctor if you notice any other effects.
Do not be alarmed by this list of possible side effects. You may not experience any of them.
FOSAMAX PLUS is not addictive.
After using FOSAMAX PLUS
Storage
Keep your tablets in the blister pack until it is time to take them. If you take the tablets out of the blister pack they may not keep well.
Keep FOSAMAX PLUS in a cool dry place where the temperature stays below 30°C. Do not freeze the product. Keep the tablets away from light or moisture. Do not store FOSAMAX PLUS or any other medicine in the bathroom or near a sink. Do not leave it in the car or on window sills. Heat and dampness can destroy some medicines.
Keep it where children cannot reach it. A locked cupboard at least one-and-a-half metres above the ground is a good place to store medicines.
Disposal
If your doctor tells you to stop taking FOSAMAX PLUS, or the tablets have passed their expiry date, ask your pharmacist what to do with any that are left over.
Product description
What it looks like
FOSAMAX PLUS comes in two strengths of tablets, each containing 70mg alendronate but with different strengths of colecalciferol (vitamin D3), either 70 micrograms (2800 IU) or 140 micrograms (5600 IU):
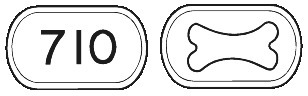
FOSAMAX PLUS (70mg/70 micrograms) comes as a white to off-white, modified capsule-shaped tablet with the outline of a bone image on one side and "710" on the other.
FOSAMAX PLUS 70mg/140 micrograms: comes as a white to off-white, modified-rectangle shaped tablet with "270" on one side and a bone image on the other.
A box of tablets contains 4 tablets (trade pack).
Ingredients
Active ingredients:
FOSAMAX PLUS (70 mg/70 micrograms) Once Weekly Tablets
- alendronate sodium equivalent to 70 mg alendronic acid per tablet
- colecalciferol 70 micrograms (2800 IU vitamin D3) per tablet
FOSAMAX PLUS 70mg/140 micrograms
- alendronate sodium equivalent to 70 mg alendronic acid per tablet
- colecalciferol 140 micrograms (5600 IU vitamin D3) per tablet
Inactive ingredients:
- microcrystalline cellulose
- lactose
- medium chain triglycerides
- gelatin
- croscarmellose sodium
- sucrose
- colloidal anhydrous silica
- magnesium stearate
- dry vitamin D3 100
- purified water
- butylated hydroxytoluene
- modified food starch
- aluminium sodium silicate.
FOSAMAX PLUS does not contain gluten, tartrazine or any other azo dyes.
Supplier
FOSAMAX PLUS is supplied in Australia by:-
Organon Pharma Pty Ltd
Building A,
26 Talavera Road,
Macquarie Park NSW 2113
This leaflet was prepared in May 2023
Australian Register Numbers:
FOSAMAX PLUS 70mg/70 micrograms (2800 IU) Once Weekly Tablets:
AUST R 113482.
FOSAMAX PLUS 70mg/140 micrograms (5600 IU) tablets:
AUST R 136846.
WPPI-OG0217A-T-012023
Published by MIMS July 2023