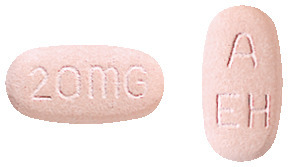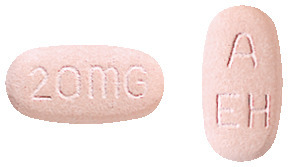1 Name of Medicine
Nexium Hp7 is a combination pack containing: esomeprazole magnesium trihydrate, amoxicillin trihydrate, clarithromycin.
2 Qualitative and Quantitative Composition
Nexium. The active ingredient in Nexium is esomeprazole magnesium trihydrate, a substituted benzimidazole. Nexium 20 mg tablets contain esomeprazole magnesium trihydrate 22.3 mg as the active ingredient.
Excipient with known effect. Sugars.
Amoxil. The active ingredient in Amoxil is amoxicillin trihydrate. Amoxil 500 mg capsule contains amoxicillin trihydrate equivalent to amoxicillin 500 mg.
Klacid. The active ingredient in Klacid is clarithromycin. Klacid tablets contain clarithromycin 500 mg.
Excipient with known effect. Sorbates.
For the full list of excipients, see Section 6.1 List of Excipients.
3 Pharmaceutical Form
Nexium Hp7 consists of:
Nexium 20 mg enteric coated tablets which are light pink, oblong, biconvex, film-coated tablets;
Amoxil 500 mg capsules which are red/yellow, hard, gelatin capsules;
Klacid 500 mg tablets which are pale yellow, film-coated ovaloid tablets.
4 Clinical Particulars
4.9 Overdose
Esomeprazole. The symptoms described in connection with deliberate esomeprazole overdose (limited experience of doses in excess of 240 mg/day) are transient. Single doses of 80 mg esomeprazole were uneventful. No specific antidote is known. Esomeprazole is extensively protein bound and is therefore not readily dialyzable. As in any case of overdose, treatment should be symptomatic and general supportive measures should be utilised.
Clarithromycin. Reports indicate that the ingestion of large amounts of clarithromycin can be expected to produce pronounced gastrointestinal symptoms. Severe liver toxicity, including cholestatic jaundice may occur. One patient who had a history of bipolar disorder ingested eight grams of clarithromycin and showed altered mental status, paranoid behaviour, hypokalaemia and hypoxemia.
There is no known antidote. Treatment consists of prompt elimination of the unabsorbed drug and supportive measures. As with other macrolides, clarithromycin serum levels are not expected to be appreciably affected by haemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis.
Amoxicillin. Gastrointestinal effects such as nausea, vomiting and diarrhoea may be evident and symptoms of water/electrolyte imbalance should be treated symptomatically. During the administration of high doses of amoxicillin, adequate fluid intake and urinary output must be maintained to minimise the possibility of amoxicillin crystalluria. Amoxicillin can be removed from the circulation by haemodialysis.
For information on the management of overdose, contact the Poisons Information Centre on 13 11 26 (Australia).
5 Pharmacological Properties
5.3 Preclinical Safety Data
Genotoxicity. Esomeprazole. Preclinical bridging studies between the enantiomer esomeprazole and the racemate (omeprazole) showed that these compounds are pharmacologically and toxicologically similar at equivalent systemic exposure. Thus, the extensive preclinical database for omeprazole is also relevant for the safety assessment of esomeprazole.
Esomeprazole was negative in a bacterial gene mutation assay. In clastogenicity tests, esomeprazole was positive (as was omeprazole) in an in vitro chromosome aberration test in human lymphocytes. However, two in vivo tests (a mouse micronucleus test and an in vivo chromosome aberration test in rat bone marrow) in the presence of long and high systemic exposure to esomeprazole, showed that esomeprazole was not clastogenic under in vivo conditions. Exposure levels in man are well below those at which clastogenic effects occurred in vitro.
Carcinogenicity. Esomeprazole. No carcinogenicity studies have been conducted on esomeprazole. However, omeprazole (the racemate) produced enterochromaffin-like (ECL) cell hyperplasia and gastric carcinoids in rats. In a 104-week study in rats, carcinoids were observed at doses (on a mg/m2 basis) which ranged from 0.4 to 30-fold the maximum clinical dose. However, a no-effect dose level was not determined in female rats. A similar effect was not observed in a 78-week mouse carcinogenicity study with omeprazole. These gastric effects in the rat are believed to be the result of sustained, pronounced hypergastrinaemia secondary to reduced production of gastric acid. Similar effects are elicited by other proton pump inhibitors, H2-receptor antagonists and by partial fundectomy.
Clarithromycin. Clarithromycin gave negative results in a battery of mutagenicity studies with the exception of a positive result in an in vitro chromosome aberration assay. Long term studies in animals have not been performed to assess carcinogenic potential.
6 Pharmaceutical Particulars
6.7 Physicochemical Properties
Chemical structure. Nexium. The chemical name is di-(S)-5-methoxy-2-[[(4-methoxy-3,5-dimethyl-2-pyridinyl) methyl] sulfinyl]-1H-benzimidazole magnesium salt trihydrate. Esomeprazole is the S-isomer of omeprazole. It is optically stable in vivo, with negligible conversion to the R-isomer.
The chemical structure for esomeprazole magnesium trihydrate is:
https://stagingapi.mims.com/au/public/v2/images/fullchemgif/CSESOMEP.gif Amoxil. The chemical name of amoxicillin is (2S,5R,6R)-6-[(R)-2-amino-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl) acetamido]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0] heptane-2-carboxylic acid. Amoxicillin trihydrate is a white or almost white, crystalline powder, which is slightly soluble in water and in ethanol (96%) and is practically insoluble in chloroform, in ether, and in fixed oils.
The chemical structure for amoxicillin trihydrate is:
https://stagingapi.mims.com/au/public/v2/images/fullchemgif/CSAMOXTR.gif Klacid. The chemical name of clarithromycin is 6-0-methylerythromycin A. Clarithromycin is a white to off-white crystalline powder, which is soluble in acetone, slightly soluble in methanol, ethanol and acetonitrile and practically insoluble in water.
The chemical structure for clarithromycin is:
https://stagingapi.mims.com/au/public/v2/images/fullchemgif/CSCLARIT.gif CAS number. The CAS number for esomeprazole is 217087-09-7.
The CAS number for amoxicillin trihydrate is 61336-70-7.
The CAS number for clarithromycin is 81103-11-9.
7 Medicine Schedule (Poisons Standard)
Schedule 4 - Prescription Only Medicine.
Summary Table of Changes
https://stagingapi.mims.com/au/public/v2/images/fulltablegif/NEXHP7ST.gif