1 Name of Medicine
Paracetamol.
2 Qualitative and Quantitative Composition
Panamax Tablets. Each tablet contains paracetamol 500 mg.
Excipients with known effect. Potassium sorbate.
Panamax Elixir. Each 5 mL contains paracetamol 120 mg.
Excipients with known effect. Benzoic acid, potassium sorbate, saccharin sodium.
Panamax 240 Elixir. Each 5 mL contains paracetamol 240 mg.
Excipients with known effect. Benzoic acid, potassium sorbate, saccharin sodium, sorbitol solution (70 per cent) (non-crystallising).
For the full list of excipients, see Section 6.1 List of Excipients.
3 Pharmaceutical Form
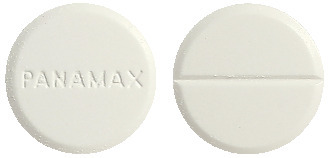
Panamax Tablets. Flat, round, scored, white tablet with bevelled edges, front face marking 'PANAMAX' with break line on the reverse.
Panamax Elixir. Clear, red coloured syrup liquid with a fruity odour and taste.
Panamax 240 Elixir. Clear light red coloured syrupy liquid.
4 Clinical Particulars
4.9 Overdose
Elderly persons, small children, patients with liver disorders, chronic alcohol consumption or chronic malnutrition, as well as patients concomitantly treated with enzyme-inducing drugs are at an increased risk of intoxication, including fatal outcome.
Symptoms. Toxic symptoms include vomiting, abdominal pain, hypotension and sweating. Nausea, vomiting, anorexia, pallor and abdominal pain generally appear during the first 24 hours of overdosage with paracetamol. Overdosage with paracetamol may cause hepatic cytolysis which can lead to hepatocellular insufficiency, gastrointestinal bleeding, metabolic acidosis, encephalopathy, disseminated intravascular coagulation, coma and death. Increased levels of hepatic transaminases, lactate dehydrogenase and bilirubin with a reduction in prothrombin level can appear 12 to 48 hours after acute overdosage. Overdosage can also lead to pancreatitis, acute renal failure and pancytopenia. The most serious adverse effect of acute overdosage of paracetamol is a dose dependent, potentially fatal hepatic necrosis. In adults, hepatotoxicity may occur after ingestion of a single dose of 12 g (24 tablets) of paracetamol; a dose of 25 g (50 tablets) or more is potentially fatal. Symptoms during the first 2 days of acute poisoning by paracetamol do not reflect the potential seriousness of the intoxication. Major manifestations of liver failure such as jaundice, hypoglycaemia and metabolic acidosis may take at least 3 days to develop.
Treatment. Despite lack of significant early symptoms, patients should be referred to hospital urgently for immediate medical attention.
Determinations of the plasma concentration of paracetamol are recommended.
Plasma concentration of paracetamol should be measured at 4 hours or later after ingestion (earlier concentrations are unreliable).
Where paracetamol intoxication is suspected, intravenous administration of SH group donators such as acetylcysteine within the first 10 hours after ingestion is indicated. Although acetylcysteine is most effective if initiated within this period, it can still offer some degree of protection if given as late as 48 hours after ingestion; in this case it is taken for longer.
If the history suggests that 12 g paracetamol or more has been ingested, administer one of the following antidotes.
Acetylcysteine 20% i.v. Administer intravenously, 20% acetylcysteine immediately without waiting for positive urine test or plasma level results. For dosage instructions refer to the acetylcysteine 20% i.v. product information.
Oral methionine. For dosage instructions refer to the methionine product information.
Further measures will depend on the severity, nature and course of clinical symptoms of intoxication and should follow standard intensive care protocols.
For information on the management of overdose, contact the Poisons Information Centre on 13 11 26 (Australia).
5 Pharmacological Properties
5.3 Preclinical Safety Data
Genotoxicity. No data available.
Carcinogenicity. No data available.
6 Pharmaceutical Particulars
6.7 Physicochemical Properties
Paracetamol is a white or almost white, crystalline powder. It is sparingly soluble in water, freely soluble in alcohol and very slightly soluble in methylene chloride. It has a melting point between 168°C and 172°C.
Chemical structure.
https://stagingapi.mims.com/au/public/v2/images/fullchemgif/CSPARCET.gif MW: 151.17.
Chemical formula. C8H9NO2.
Chemical name. N-(4-Hydroxyphenyl) acetamide.
CAS number. 103-90-2.
7 Medicine Schedule (Poisons Standard)
Pharmacy Medicine (Schedule 2).
Summary Table of Changes
https://stagingapi.mims.com/au/public/v2/images/fulltablegif/PANAMAST.gif