What is in this leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine This leaflet answers some common questions about PREZCOBIX tablets. It does not contain all the available information. It does not take the place of talking to your doctor or pharmacist.
All medicines have risks and benefits. Your doctor has weighed the risks of you being given PREZCOBIX against the benefits this medicine is expected to have for you.
If you have any concerns about being given PREZCOBIX ask your doctor.
Keep this leaflet while you are taking PREZCOBIX. You may need to read it again.
What PREZCOBIX is used for
PREZCOBIX is used to treat adults, who are infected by HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus).
PREZCOBIX contains two active ingredients which work in combination for the treatment of HIV. These active ingredients are darunavir and cobicistat.
Darunavir is an antiretroviral medicine. It belongs to a group of medicines called protease inhibitors. Darunavir works by reducing the amount of HIV in your body. Reducing the amount of HIV in your blood improves your immune system, and reduces the risk of developing illnesses as a result of HIV infection.
Cobicistat is a type of medicine called a pharmacokinetic enhancer (or "booster"). Cobicistat helps increase the levels of darunavir, the HIV medicine in your body.
PREZCOBIX can be taken with other anti-HIV medicines. Your doctor will discuss with you which combination of medicines will work best with PREZCOBIX.
Ask your doctor if you have any questions about why PREZCOBIX has been prescribed for you.
This medicine is available only with a doctor's prescription.
Before you take PREZCOBIX
When you must not use it:
Do not take PREZCOBIX:
- if you are allergic (hypersensitive) to darunavir, cobicistat or any of the other ingredients of PREZCOBIXlisted in the Ingredient section of this document.
- Symptoms of an allergic reaction may include rash, itching or hives on the skin, shortness of breath, wheezing or difficulty breathing, swelling of the face, lips, tongue or other parts of the body.
Do not take PREZCOBIX:
- if the packaging is torn or shows signs of tampering.
- if the expiry date (month and year) printed on the pack has passed. If you take PREZCOBIX after the expiry date it may not work.
PREZCOBIX should not be given to children younger than 18 years of age.
Do not combine PREZCOBIX with any of the following medicines:
- alfuzosin (to treat an enlarged prostate)
- astemizole or terfenadine (to treat allergy symptoms)
- cisapride (to treat some stomach conditions)
- colchicine (to treat gout) if you have renal/hepatic impairment
- amiodarone, bepridil, disopyramide, flecainide, systemic lidocaine, mexiletine, propafenone, quinidine or dronedarone (to treat irregular heartbeats)
- ivabradine or ranolazine (to treat heart disease)
- lomitapide, lovastatin or simvastatin (to lower cholesterol levels)
- midazolam or triazolam (to treat trouble with sleeping and/or anxiety)
- lurasidone or pimozide (to treat psychiatric conditions)
- apixaban (used to reduce blood clotting)
- carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin (medicines to prevent seizures or to treat trigeminal neuralgia)
- ergot alkaloids i.e. dihydroergotamine, ergonovine, ergotamine, methylergonovine (to treat migraine and headaches)
- sildenafil (to treat pulmonary arterial hypertension)
- rifampin (to treat some infections such as tuberculosis)
- elbasvir/grazoprevir (to treat hepatitis C)
- products that contain St John's wort (Hypericum perforatum)
- naloxegol (to treat opioid induced constipation)
- dapoxetine (to treat premature ejaculation)
If you are taking any of these, ask your doctor about switching to another medicine.
This not a complete list of medicines. Therefore, tell your doctor about all medicines you take.
There are other medicines that you need to be careful of when taking PREZCOBIX (see Taking other medicines).
Before you start to use it:
Take special care with PREZCOBIX:
PREZCOBIX is not a cure for HIV infection.
PREZCOBIX does not reduce the risk of passing HIV to others through sexual contact or blood. Therefore, you must continue to use appropriate precautions to prevent passing HIV on to others.
People taking PREZCOBIX can still develop infections or other illnesses associated with HIV. You should continue to keep in regular contact with your doctor and to monitor your health while taking PREZCOBIX.
Tell your doctor if you have or have had any medical conditions, especially the following:
- Kidney problems or are undergoing kidney dialysis treatment.
-
Problems with your liver, including hepatitis B and C.
Your doctor may need to evaluate your liver before deciding if you can take PREZCOBIX. -
Diabetes.
PREZCOBIX, like some other anti-HIV medicines, might increase sugar levels in the blood. -
Haemophilia.
Anti-HIV medicines, such as PREZCOBIX, might increase the risk of bleeding in patients with this blood clotting disorder. - Are allergic to foods, dyes, preservatives, sulfa medicines (sulphonamides) or any other medicines.
Tell your doctor immediately if you are pregnant or breastfeeding, or intend to become pregnant or breastfeed.
Do not take PREZCOBIX if you are pregnant or breastfeeding. It is recommended that HIV infected women should not breastfeed their infants because of the possibility of your baby becoming infected with HIV through your breast milk and because of the unknown effects of the medicine on your baby. If you are a woman who has or will have a baby, talk with your doctor about the best way to feed your baby.
If you have not told your doctor about any of the above, tell them before you start treatment with PREZCOBIX.
Taking other medicines:
Some medicines may affect the levels of PREZCOBIX or PREZCOBIX may affect the level of other medicines in the body when they are taken at the same time as PREZCOBIX. Your doctor might want to do some additional blood tests.
For this reason, tell your doctor about all medicines you take, including medicines you can buy without a prescription from a pharmacy, supermarket or health food shop.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of medicines and show it to your doctor and pharmacist when you get a new medicine. Your doctor and your pharmacist can tell you if you can take these medicines with PREZCOBIX
- Tell your doctor if you are taking any of the following: amiodarone, bepridil, disopyramide, flecainide, systemic lidocaine, mexiletine, propafenone, quinidine, dronedarone, apixaban, midazolam, triazolam, ergot alkaloids (dihydroergotamine, ergonovine, ergotamine, methylergonovine), astemizole, terfenadine, cisapride, pimozide, lurasidone, alfuzosin, sildenafil, colchicine, lomitapide, lovastatin, simvastatin, ivabradine, ranolazine, rifampicin, elbasvir/grazoprevir, carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, products that contain St John's wort (Hypericum perforatum), naloxegol or dapoxetine. You must not take these medicines while taking PREZCOBIX.
- Tell your doctor if you take other anti-HIV medicines. PREZCOBIX can be combined with some other anti-HIV medicines while other combinations are not recommended.
-
If you take PREZCOBIX with some other medicines, the effects of PREZCOBIX or other medicines might be influenced. The dosage of some medicines may need to be changed. Some combinations are not recommended. Tell your doctor if you take any of the following:
- oestrogen-based hormonal contraceptives. PREZCOBIX might reduce the effectiveness of hormonal contraceptives. Therefore, additional or alternative (non-hormonal) methods of contraception are recommended. If you take a contraceptive containing drospirenone your potassium levels might become elevated.
- medicines for heart disease (amlodipine, diltiazem, felodipine, nifedipine, nicardipine, tadalafil, verapamil).
- medicines to treat certain heart disorders (digoxin, carvedilol, metoprolol, timolol, bosentan)
- medicines used to reduce clotting of the blood (dabigatran etexcilate, edoxaban, rivaroxaban, warfarin) or to prevent blood clots (ticagrelor, clopidogrel).
- medicines to lower cholesterol levels (pravastatin, atorvastatin, rosuvastatin, pitavastatin). The risk of muscle tissue disorder might be increased. Atorvastatin, rosuvastatin, or pravastatin, at a reduced starting dose, could be used as an alternative.
- medicines for your immune system (cyclosporine, tacrolimus, sirolimus, everolimus, rapamycin). Your doctor might want to do some additional tests.
- medicines to treat asthma (salmeterol).
- corticosteroids (betamethasone, budesonide, dexamethasone, fluticasone, mometasone, prednisone, triamcinolone).
- medicines to treat cancer (dasatinib, everolimus, irinotecan, nilotinib, vinblastine, vincristine).
- medicines to treat pain (fentanyl, oxycodone, tramadol).
- medicines to treat narcotic dependence (buprenorphine/naloxone, methadone).
- medicines to treat malaria (artemether/lumefantrine).
- medicines to treat hepatitis C (telaprevir, boceprevir, glecaprevir/pibrentasvir).
- medicines to treat urinary disorders (fesoterodine, solifenacin).
- medicines to treat nausea and vomiting (domperidone).
- medicines to treat fungal infections (clotrimazole, fluconazole, isavuconazole, itraconazole, ketoconazole, posaconazole, voriconazole).
- medicines to treat some infections such as tuberculosis (rifabutin, rifapentine).
- medicines against bacterial infections (clarithromycin, erythromycin and telithromycin).
- medicines to treat gout (colchicine). If you have renal/hepatic impairment, do not take colchicine with PREZCOBIX.
- medicines for erectile dysfunction (avanafil, vardenafil, tadalafil, sildenafil).
- medicines to treat depression and anxiety (paroxetine, sertraline, amitriptyline, desipramine, imipramine, nortriptyline, and trazodone).
- sedatives (buspirone, clorazepate, diazepam, estazolam, flurazepam, zolpidem).
- medicines to treat psychiatric conditions (risperidone, thioridazine, quetiapine, perphenazine).
- medicines to prevent seizures or to treat trigeminal neuralgia (oxcarbazepine, clonazepam).
- medicines to treat excessive sleepiness (armodafinil, modafinil).
This is not a complete list of medicines. Tell your doctor about all medicines that you are taking.
Taking PREZCOBIX
Adults
Always use PREZCOBIX exactly as your doctor has told you. You must check with your doctor if you are not sure.
Make sure that you always have enough PREZCOBIX available so that you don't run out. For example, in case you cannot return home, need to travel or stay in a hospital.
How much PREZCOBIX to take:
The usual dose of PREZCOBIX is one tablet orally, once daily with food.
You must take PREZCOBIX every day and always with food. PREZCOBIX cannot work properly without food. You must eat a meal or a snack within 30 minutes prior to taking your PREZCOBIX. The type of food is not important.
Even if you feel better, do not stop taking PREZCOBIX without talking to your doctor.
Instructions:
- Take PREZCOBIX with food.
- Swallow the tablets with a drink such as water, milk, or any other nutritional drink.
Take your other HIV medicines used in combination with PREZCOBIX as recommended by your doctor.
Removing the child resistant cap
The plastic bottle comes with a child resistant cap and should be opened as follows:
- Push the plastic screw cap down while turning it counter clockwise.
- Remove the unscrewed cap.
What do I do if I forget to take PREZCOBIX?
If you forget to take PREZCOBIX
If you notice within 12 hours, you must take the tablets immediately. Always take with food. If you notice after 12 hours, then skip the intake and take the next doses as usual. Do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose.
Please refer to your doctor for instructions on missed doses of other HIV medicines used in combination with PREZCOBIX.
What do I do if I take too much? (overdose):
If you think you or anybody else has taken too much PREZCOBIX, contact your doctor, pharmacist or the Poisons Information Centre who will advise you what to do.
You can contact the Poisons Information Centre by dialling:
- Australia: 13 11 26
Or go to the accident and emergency department at your nearest hospital. Do this even if there are no signs of discomfort or poisoning. This may need urgent medical attention.
While you are taking PREZCOBIX
Things you must do:
Do not stop taking PREZCOBIX without talking to your doctor first.
Tell your doctor if you have any medical conditions, especially the following:
-
Symptoms of infection.
In some patients with advanced HIV infection and a history of opportunistic infection, signs and symptoms of inflammation from previous infections may occur soon after anti-HIV treatment is started. It is believed that these symptoms are due to an improvement in the body's immune response. This improvement enables the body to fight infections that may have been present prior to taking PREZCOBIX, with no obvious symptoms.
HIV therapy may increase your sense of well being. Even when you feel better, do not stop taking PREZCOBIX. Talk to your doctor first.
Be sure to keep all your doctor's appointments so your progress can be checked. Your doctor will want to do some blood, urine and other tests from time to time to check on your progress.
Be sure to follow up your doctor's instructions about other medicines you should take, and other things you should do.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist if you have any questions.
Tell any other doctors and pharmacists who are treating you that you are taking PREZCOBIX. If you are undergoing anaesthesia, tell your anaesthetist that you are taking PREZCOBIX.
If you are about to be started on any new medicines, tell your doctor or pharmacist that you are taking PREZCOBIX.
If you become pregnant while taking PREZCOBIX, tell your doctor immediately. You must not take PREZCOBIX if you are pregnant.
If you have any further questions on the use of this product, ask your doctor.
Things you must not do:
- Do not breastfeed. See "Before you start to use it".
- Avoid doing things that can spread HIV infection since PREZCOBIX does not stop you from passing the HIV infection to others:
- Do not share needles or other injection equipment.
- Do not share personal items that can have blood or body fluids on them, like toothbrushes or razor blades.
- Do not have any kind of sex without protection. Always practise safer sex by using a latex or polyurethane condom or other barrier to reduce the chance of passing the infection through semen, vaginal secretions, or blood.
- Do not take PREZCOBIX if the packaging is torn or shows signs of tampering.
Things to be careful of
Driving and using machines
Do not operate machines or drive if you feel dizzy after taking PREZCOBIX.
Side Effects
Like all medicines, PREZCOBIX can have side effects. Some of these effects may be serious.
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you do not feel well while you are being treated with PREZCOBIX.
When treating HIV infection, it is not always easy to identify what side effects are caused by PREZCOBIX, which are caused by other medicines you are taking, or which are caused by the HIV infection itself.
The most common side effects are:
- nausea, vomiting
- headache
- abdominal pain, diarrhoea
- passing wind
- rash (see information below), itching or hives on the skin
PREZCOBIX may change some values of your blood chemistry. These can be seen in the results of blood tests. Your doctor will explain these to you.
Liver problems that may occasionally be severe have been reported. Your doctor should do blood tests prior to initiating PREZCOBIX. If you have chronic hepatitis B or C infection, your doctor should check your blood tests more often because you have an increased chance of developing liver problems. Talk to your doctor about the signs and symptoms of liver problems. These may include yellowing of your skin or whites of your eyes, dark (tea coloured) urine, pale coloured stools (bowel movements), nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, or pain, aching, or sensitivity on your right side below your ribs.
Skin rash has been reported in patients receiving PREZCOBIX. Occasionally a rash can be severe or potentially life threatening. In patients taking PREZCOBIX and raltegravir, rashes (generally mild or moderate) may occur more frequently than in patients taking either drug separately. It is important to consult your doctor if you develop a rash. Your doctor will advise you how to deal with your symptoms or whether PREZCOBIX must be stopped.
Tell your doctor if you experience the following side effects:
- loss of appetite
- increased blood fat levels
- diabetes
- symptoms of infection
Some side effects are typical for anti-HIV medicines in the same family as PREZCOBIX. These are:
- raised blood sugar and worsening of diabetes.
- immune reactivation syndrome. In some patients with advanced HIV infection (AIDS) and a history of opportunistic infection, signs and symptoms of inflammation from previous infections may occur soon after anti-HIV treatment is started, including PREZCOBIX. In addition to the opportunistic infections, autoimmune disorders (a condition that occurs when the immune system attacks healthy body tissue) may also occur after you start taking medicines for treatment of your HIV infection. Autoimmune disorders may occur many months after the start of treatment.
- increased bleeding in patients with haemophilia.
- muscle pain, tenderness or weakness. On rare occasions, these muscle disorders have been serious.
If you experience any of these side effects and they worry you, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet, please tell your doctor.
Tell your doctor if you notice signs or symptoms of infections, such as a fever or rashes. Some people with HIV who have had infections in the past may experience a return of symptoms soon after taking anti-HIV medicines.
If you think you are having an allergic reaction to PREZCOBIX, tell your doctor immediately or go to Accident and Emergency at your nearest hospital.
Symptoms usually include some or all of the following:
- rash, itching or hives on the skin
- shortness of breath, wheezing or difficulty breathing
- swelling of the face, lips, tongue or other parts of the body.
Other side effects not listed above may also occur in some people.
Product Description
Storage
PREZCOBIX tablets should be kept out of reach of children, in a location where the temperature stays below 30°C.
What it looks like:
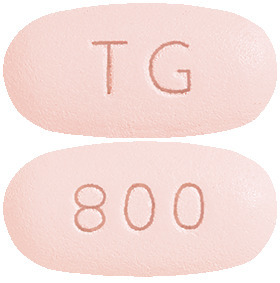
PREZCOBIX 800/150 mg film-coated tablet: Pink oval-shaped tablet, debossed with "800" on one side and "TG" on the opposite side. Each plastic bottle contains 30 tablets.
Ingredients
Active ingredients:
- darunavir 800 mg (as darunavir ethanolate)
- cobicistat 150 mg
Other ingredients:
- hypromellose
- silicon dioxide
- microcrystalline cellulose
- crospovidone
- magnesium stearate
- Opadry II complete film coating system 85F140053 Pink (ARTG PI No. 109886) (Film Coating)
Sponsor
JANSSEN-CILAG Pty Ltd
1-5 Khartoum Rd
Macquarie Park NSW 2113 Australia
Telephone: 1800 226 334

Registration numbers
800/150 mg tablet: AUST R 231198
This leaflet was prepared in 27 March 2023.
® PREZCOBIX is a registered trademark of Janssen-Cilag Pty Ltd.
Published by MIMS May 2023