What is in this leaflet
This leaflet answers some common questions about Signifor.
The information in this leaflet was last updated on the date listed on the final page. More recent information on the medicine may be available.
You should ensure that you speak to your pharmacist or doctor to obtain the most up to date information on the medicine. Those updates may contain important information about the medicine and its use of which you should be aware.
It does not contain all the available information. It does not take the place of talking to your doctor or pharmacist.
All medicines have risks and benefits. Your doctor has weighed the risks of you taking this medicine against the benefits they expect it will provide.
If you have any concerns about this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Keep this leaflet with the medicine. You may need to read it again.
What Signifor is used for
Signifor is used to treat Cushing's Disease, a condition caused by an enlargement in the pituitary gland (pituitary adenoma, a benign tumour) which produces too much of a hormone called adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). This overproduction of ACTH causes the body to produce too much of another hormone called cortisol. Too much cortisol leads to a variety of signs and symptoms such as weight gain with abdominal obesity, moon-shaped face, easy bruising, menstrual abnormalities, excessive body and facial hair, muscle wasting with generalized weakness and tiredness, depression and decreased libido. Signifor is designed to block the production of ACTH and therefore cortisol and help to reduce the symptoms caused by excess of cortisol.
Signifor contains pasireotide, a synthetic substance that mimics the action of somatostatin, a substance normally found in the human body, which can block the production of certain hormones such as ACTH. The advantage of pasireotide over somatostatin is that its effect is stronger and lasts longer.
Ask your doctor if you have any questions about why this medicine has been prescribed for you. Your doctor may have prescribed it for another reason.
This medicine is not addictive.
This medicine is available only with a doctor's prescription.
Before you inject Signifor
When you must not take it
Do not take Signifor if you have an allergy to pasireotide, the active ingredient, or to any of the other ingredients listed at the end of this leaflet. Some of the symptoms of an allergic reaction may include shortness of breath, wheezing or difficulty breathing; swelling of the face, lips, tongue or other parts of the body; rash, itching or hives on the skin.
Do not take this medicine if you suffer from severe liver disorder.
Do not take this medicine after the expiry date printed on the pack or if the packaging is torn or shows signs of tampering. In that case, return it to your pharmacist.
Before you start using it
Tell your doctor if you have allergies to any other medicines, foods, preservatives or dyes.
Tell your doctor if you have, or have had, any of the following medical conditions:
- problems with your blood glucose levels, either too high (hyperglycemia/diabetes) or too low (hypoglycaemia)
- problems with your liver
- a heart disorder or a heart rhythm disorder, such as an irregular heartbeat or an abnormal electrical signal called "prolongation of the QT interval, or QT prolongation"
- low levels of potassium or magnesium in your blood
- gallstones.
Tell your doctor if you are taking, or have ever taken, medicines to:
- control your heart rate (antiarrhythmics) or medicines that may have an unwanted effect on the function of the heart beat (QT prolongation)
- control your blood pressure (such as beta-blockers or calcium channel blockers) or agents to control electrolytes (potassium, magnesium) balance in your body
Your doctor may want to take special precautions.
Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant or are breast-feeding. Signifor is not recommended during pregnancy. Your doctor will discuss with you the potential risk of taking Signifor during pregnancy.
You should not breastfeed your child while using Signifor. It is not known if Signifor passes into breast milk.
Women of child-bearing potential should use an effective method of contraception during treatment. Ask your doctor about the need for contraception before you start taking Signifor.
Taking other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking any other medicines, including any that you buy without a prescription from your pharmacy, supermarket or health food shop.
Some medicines and Signifor may interfere with each other. These include:
Anti-arrhythmics used to treat irregular heart rate such as:
- amiodarone
- disopyramide
- procainamide
- sotalol
- quinidine
Medicines that may have an unwanted effect on the function of the heart (QT prolongation) such as:
- ketoconazole
- chloroquine
- halofantrine
- clarithromycin
- haloperidol
- methadone
- bepridil
- pimozide
Certain other medicines, such as:
- cyclosporin
- terfenadine
- bromocriptine
You may need to take different medicines. Your doctor and pharmacist have more information.
If you have not told your doctor about any of these things, tell him/her before you start taking this medicine.
How to inject Signifor
Your doctor or nurse will instruct you on how to inject yourself with Signifor.
Follow all directions given to you by your doctor or nurse. They may differ from the information contained in this leaflet.
If you have any questions, contact your doctor, nurse or pharmacist.
How much to inject
The recommended dosage range of Signifor is 300 to 900 micrograms (mcg) injected under the skin (subcutaneous) two times a day (approximately every 12 hours).
If you have high blood glucose levels or liver problems before you start using Signifor, your doctor may want to start your treatment with a lower dose two times a day.
Your doctor will monitor how you respond to the treatment with Signifor and may ask you to change to a higher or lower dose.
How to inject it
This medicine comes in an ampoule ie a small glass container. Your doctor or nurse will have instructed you on how to use Signifor ampoules. However before using the ampoule, please read the following instructions carefully. If you are not sure about how to give the injection or you have any questions, please ask your doctor or nurse for help.
The injection can be prepared using either two different needles to draw up and inject the solution or one short fine injection needle for both steps. Based on the local clinical practice, your doctor or nurse will tell you which method to use. Please follow their instructions.
Store Signifor ampoules according to the storage condition listed at the bottom of this leaflet.
Important Safety Information
- Always use new disposable needles and syringes every time you give yourself an injection.
- Use syringes and needles only once. NEVER share needles and syringes with someone else.
- Carefully inspect the ampoule prior to use. DO NOT USE if it is broken or if the liquid looks cloudy, coloured or contains particles. In all these cases, return the entire pack to the pharmacy.
- For sterility reasons, ampoules should be opened just prior to administration.
- This medicine is for single use in one patient only. Discard any residue.
Signifor is intended for subcutaneous use. This means that it is injected through a short needle into the fatty tissue just under the skin.
The injection site is the place on your body where you are going to give yourself the injection.
The TOP OF THIGHS and the ABDOMEN are recommended areas for subcutaneous injection. It is important to rotate the site of your injections, that is, you should choose a different site each time you inject.
You should also avoid injections at sites that are sore, where the skin is irritated, the navel, waistline, bruises and scars.
To reduce local discomfort, it is recommended that the solution should be at room temperature before injection.
Do not inject Signifor solution for injection into a vein or muscle.
PREPARING A DOSE
- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water.
- Take ampoule out of the box and carefully inspect the ampoule (as above).
- Read the label first. Check the dose on the ampoule is the dose your doctor has prescribed for you.
- Signifor solution for injection is filled in a break-off ampoule. The coloured dot on the top part marks the position of the breaking point on the neck of the ampoule.
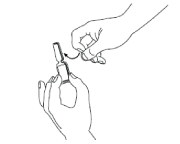
TAP the ampoule with your finger in order to make sure there is no liquid in the top part when you open the ampoule.
- Recommended procedure:
Hold the ampoule in an upright position with the coloured dot facing away from you. Hold the base of the ampoule in one hand. Keeping your thumbs together above and below the neck, break off the top of the ampoule at the breaking point.
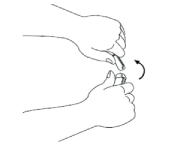
Once the ampoule is open, put it upright on a clean, flat surface.
- Take the sterile syringe and attach the needle to it.
If you have been told to use two needles, you should use the long thick blunt drawing up needle for this step.
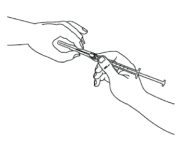
Before you proceed to the next step, clean the injection site with an alcohol wipe or similar.
- Remove the cover from the needle. Put the needle into the ampoule and pull the plunger to draw up the entire contents of the ampoule into the syringe.
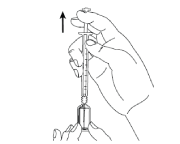
If you have been told to use two needles, you should now replace the long needle with the short giving needle.
- Hold the syringe in one hand between two fingers with your thumb at the bottom of the plunger. Tap the syringe with your fingers to get rid of air bubbles. Make sure there is no air bubble in the syringe by pressing the plunger until the first drop appears on the tip of the needle.
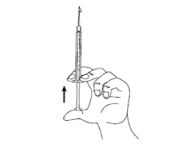
Do not let the needle touch anything. You are now ready to inject.
INJECTING A DOSE
- Gently pinch the skin at the injection site and holding the needle at an angle advised by your doctor or nurse, insert it into the skin.
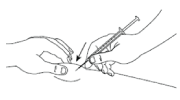
- Keeping your skin pinched, slowly press down the plunger as far as it will go until all the solution is injected. Hold this position for 5 seconds.
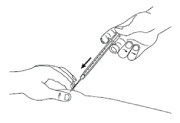
- Slowly release the skin and gently pull the needle out.
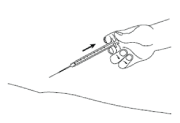
IMPORTANT: If you injected yourself, put the cover back on the needle. If a carer has carried out the injection, they should not recap the needle in case of needle-stick injury.
- Dispose of every used syringe and needle immediately in a standard approved sharps container. Any unused medicine or waste material should be disposed of in a manner that meets local requirements. Your doctor or nurse can provide disposal information as well as your local council.
Seek advice if you plan to travel.
When to inject it
Take Signifor twice a day (approximately every 12 hours).
Using Signifor at the same time each day will help you remember when to use your medicine.
How long to inject it
Do not stop taking Signifor unless your doctor tells you to. This medicine helps to control your condition, but does not cure it. If you interrupt your treatment with Signifor your cortisol level may increase again and your symptoms may come back. Therefore, you should not stop using Signifor without discussing it with your doctor.
If you forget to inject it
If you forget to administer a dose of Signifor simply take your next injection at the scheduled time.
Do not take a double dose to make up for the dose that you missed. This may increase the chance of you getting an unwanted side effect.
If you have trouble remembering to take your medicine, ask your pharmacist for some hints.
If you inject too much (overdose)
Immediately telephone your doctor or the Poisons Information Centre (telephone 13 11 26) for advice, or go to Accident and Emergency at the nearest hospital, if you think that you or anyone else may have taken too much Signifor. Do this even if there are no signs of discomfort or poisoning. Keep the telephone numbers for these places handy.
While you are using Signifor
Things you must do
If you experience extreme weakness, weight loss, nausea, vomiting and low blood pressure seek urgent medical attention. These are some of the signs and symptoms associated with a lack of cortisol.
Keep all of your doctor's appointments so that your progress can be checked.
Your doctor may wish to monitor the following:
- your blood glucose levels
You may need to start taking or adjust your anti-diabetic medication. - your heart rate using a test called electrocardiogram or ECG
If you take a heart medication, your doctor may also need to adjust its dosage. - your gallbladder, liver enzymes and pituitary hormones periodically
If you become pregnant while taking this medicine, tell your doctor immediately. It may affect your developing baby. Your doctor will discuss the risks and benefits of continuing treatment in this case.
If you are about to be started on any new medicine, remind your doctor and pharmacist that you are taking this medicine.
Tell any other doctors, dentists, and pharmacists who treat you that you are taking this medicine.
Things you must not do
Do not give this medicine to anyone else, even if their condition seems similar to yours.
Do not use it to treat any other complaints unless your doctor tells you to.
Things to be careful of
Be careful driving, operating machinery or doing jobs that require you to be alert until you know how Signifor affects you.
Side effects
Tell your doctor or pharmacist as soon as possible if you do not feel well while you are taking Signifor even if you do not think it is connected with the medicine.
All medicines can have side effects. Sometimes they are serious, but most of the time they are not. You may need medical treatment if you get some of the side effects.
Do not be alarmed by the following lists of side effects. You may not experience any of them.
Most of the side effects are mild to moderate and will generally disappear after a few days to a few weeks of treatment.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist to answer any questions you may have.
Tell your doctor as soon as possible if you notice any of the following:
- low cortisol levels (you may experience extreme weakness, weight loss, nausea, vomiting, low blood pressure)
- high blood glucose level (you may experience excessive thirst, high urine output, increased appetite with weight loss, tiredness, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fruity scented breath, trouble breathing and confusion)
- Bile flow from liver to intestine can be reduced (cholestasis). The symptoms may include yellowing of the skin/eye, dark urine, pale stool, and itching.
- low blood glucose levels
- slow heart rate
- irregular heart rate
- gallstones (you may experience sudden back pain or pain on the right side of your abdomen).
The above list includes serious side effects which require immediate medical attention.
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you notice any of the following and they worry you:
- diarrhoea
- nausea
- abdominal pain
- inflammation of gallbladder with signs of upper abdominal pain (cholecystitis).
- fatigue
- local pain at injection site
- change in glucose levels in blood
- loss of appetite
- vomiting
- headache
- dizziness
- common cold
- hair loss
- weakness
- swelling due to fluid retention
- anxiety
- flu like symptoms
- insomnia
- muscle pain
- joint pain
- itch
- constipation
- low blood pressure (hypotension)
- back pain
- dry skin
- pain in the extremities
- vertigo
- abdominal expansion
Some people may have other side effects not yet known or mentioned in this leaflet.
Some of these side effects, for example, anaemia, changes in liver function, pancreatic function, blood coagulation parameters and abnormal blood test results (sign of high level of fat in the blood) can only be found when your doctor does tests from time to time to check your progress.
After using Signifor
Storage
- Keep this medicine in the original package in order to protect it from light.
- Store it in a cool, dry place below 30°C.
- Do not leave it in the car or on window sills.
Keep this medicine where children cannot reach it. A locked cupboard at least one-and-a-half metres above the ground is a good place to store medicines.
Disposal
If your doctor tells you to stop taking this medicine or the expiry date has passed, ask your pharmacist what to do with any medicine you have left over.
Product description
What it looks like
Signifor is supplied as a solution for injection in a 1 mL one point-cut colourless glass ampoule.
Signifor comes in packs of 6, 30 or 60 ampoules. Not all pack sizes are marketed.
Ingredients
The active substance of Signifor is pasireotide. Each ampoule contains 300 micrograms (mcg) or 600 micrograms (mcg) or 900 micrograms (mcg) pasireotide. It also contains:
- mannitol
- tartaric acid
- sodium hydroxide
- water for injections
Sponsor
Signifor® is supplied in Australia by:
Recordati Rare Diseases Australia Pty Ltd
Suite 1802, Level 18, 233
Castlereagh Street,
Sydney, NSW, 2000
Australia
Phone: +61 (0) 408 061 403
rrdaustraliainfo@recordati.com
®= Registered Trademark
This leaflet was prepared in April 2022.
Australian Registration Numbers:
Signifor 300 mcg AUST R 201485
Signifor 600 mcg AUST R 201484
Signifor 900 mcg AUST R 201486
Published by MIMS September 2022
