What is in this leaflet
This leaflet answers some common questions about SOTACOR. It does not contain all the available information. It does not take the place of talking to your doctor or pharmacist.
All medicines have risks and benefits. Your doctor has weighed the risks of you using SOTACOR against the benefits they expect it will have for you.
If you have any concerns about using this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Keep this leaflet with the medicine. You may need to read it again.
What SOTACOR is used for
SOTACOR contains sotalol hydrochloride as the active ingredient which belongs to the family of drugs known as beta-blockers.
SOTACOR is used to treat “arrhythmias”, which is a problem when the heart beats too quickly or with the wrong rhythm.
SOTACOR slows down and steadies the heart beat, reducing the effort the heart has to put into pumping blood.
Ask your doctor if you have any questions about why SOTACOR has been prescribed for you. Your doctor may have prescribed it for another reason.
There is no evidence that this medicine is addictive.
SOTACOR is only available with a doctor’s prescription.
Before using it
When you must not use it
Do not use SOTACOR if you have an allergy to:
- sotalol hydrochloride
- other beta blockers
- any of the ingredients listed at the end of this leaflet
Some of the symptoms of an allergic reaction may include:
- shortness of breath, wheezing or difficulty breathing
- skin rash, itching or hives
- swelling of the face, lips, tongue or any part of the body.
Do not take SOTACOR if you have asthma.
You should not take this medicine if you have allergies, or problems with your kidneys or thyroid gland, unless you have discussed it with your doctor.
You should not take this medicine if you are pregnant or are breast feeding, or if you intend to breast feed.
If you have any problems with your heart or circulation or amount of magnesium in your blood, discuss them with your doctor.
You should not take SOTACOR with any other medicines your doctor does not know about, particularly if they are to control high blood pressure, heart conditions, depression, hayfever, allergies, infections or diabetes.
Do not take it if the expiry (EXP) date printed on the pack has passed
Do not take it if the packaging is torn of shows signs of tampering.
Talk to you doctor if you are unsure whether you should start taking this medicine.
Before you start to take it
- Make sure your doctor knows what other medicines you are already taking including ones you have bought yourself at the chemist or supermarket.
- In particular remind your doctor if you have asthma, bronchitis or any allergies such as hay fever, food allergies or are allergic to bee or wasp stings.
- Make sure your doctor is aware of any kind of heart disease, diabetes, phaeochromocytoma, kidney disease or thyroid disease that you have or have had, or if you have been told that your pulse is slow or irregular.
- Tell your doctor if you have ever had trouble with the levels of salts like potassium or magnesium in your blood.
- Remind your doctor if you are going to have surgery involving a general anaesthetic even if it is only minor.
- Tell your doctor if you are pregnant, if you are planning to become pregnant, or if you are breast feeding.
- Tell your doctor if you have been given SOTACOR (or any other beta-blocker) before and if you had any problems.
- Remind your doctor if you have hardening of the arteries (cold fingers and toes or pain in the back of your legs when you walk).
Be careful driving or operating machinery until you know how SOTACOR affects you. As with other medicines it may cause dizziness, light-headedness or drowsiness in some people. If this occurs do not drive or operate machinery or undertake any other activity that could be dangerous if you are dizzy, light-headed or drowsy.
Taking other medicines
Some medicines can affect the way SOTACOR works.
You should always tell your doctor about any other medicines you take, even those bought without a doctor’s prescription.
It is especially important that you tell your doctor if you are taking the following:
- medicines which lower blood pressure (including other beta-blockers)
- floctafenine (medicine used for the short term treatment of mild to moderate pain)
- for the treatment of certain infections (e.g. erythromycin IV, amphotericin B, pentamidine, halofantrine)
- steroids
- laxatives
- clonidine (sometimes used to treat hot flushes or headaches)
- any other medicines used to treat irregular heart rhythm or beat
- digoxin, a medicine used for heart failure
- medicines used to treat angina or other heart conditions
- antidepressants (medicines used to treat depression)
- insulin or other drugs used to control diabetes
- Medicines used to control or prevent asthma (inhalers or tablets) or to control allergies or which are used for other lung problems
- Antihistamine medicine including terfenadine and astemizole that may be used to treat hayfever, allergies or to relive symptoms of cold and flu
- quinolone antibiotics (medicines used to treat infections)
- diuretics (water tablets)
- neuromuscular blocking agents like tubocarine
- some medicine used during surgery or emergency situations, such as anaesthetics.
If you are not sure whether you are taking any of these medicines, check with your doctor of pharmacist.
How to take it
Follow all directions given to you by your doctor or pharmacist carefully. They may differ from the information contained in this leaflet.
If you do not understand the instructions on the box, ask your doctor or pharmacist for help.
How much to take
Your doctor will decide on the dose of SOTACOR tablets for you, and may need to change the dose a few times to get the best level for you.
The usual dose is 80mg to 160mg twice a day. Your doctor may need to increase this as a very few patients may need up to three to four 160mg tablets spread over a day. The dosage may need to be different if you have a kidney problem.
How to take it
You should take your tablets with water one to two hours before meals. Do not take SOTACOR with milk or meals.
How long to take it for
If you have been prescribed SOTACOR you must be sure to follow your doctors instructions carefully.
Do not stop taking SOTACOR tablets suddenly.
The dose needs to be reduced gradually over 7 to 14 days.
If you forget to take it
It is important not to miss a dose but if you do, take your next dose at the normal time and with the normal amount.
If you take too much (overdose)
Immediately telephone your doctor or the Poisons Information Centre (telephone 13 11 26) for advice, or go to Accident and Emergency at the nearest hospital, if you think that you or anyone else may have taken too much SOTACOR. Do this even if there are no signs of discomfort or poisoning. You may need medical attention.
Too much of this medicine will cause your blood pressure and heart rate to drop to dangerous levels. Serious heart problems may develop and this could be fatal.
Side Effects
Tell your doctor or pharmacist as soon as possible if you do not feel well while you are taking SOTACOR.
SOTACOR helps most people with arrhythmia, but it may have unwanted side effects in some people. Rarely, serious heart problems can develop while you are taking normal doses but you must remember that you are taking this medicine because your heart already has a serious problem. It is very important that your doctor keeps a check on your progress.
All medicines can have side effects. Sometimes they are serious, most of the time they are not. You may need medical treatment if you get some of the side effects.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist to answer any questions you may have.
Tell your doctor if you notice any of the following and they worry you:
- dizziness, lightheadedness or fainting, especially when you get up from a sitting or lying position. Getting up slowly may help.
- tiredness, lack of energy, weakness
- headache, fever
- cramps
- irritated eyes, blurred vision, worsening of eyesight, increased sensitivity of the eyes to sunlight
- feeling sick, vomiting, stomach upset, diarrhoea, wind
- change in taste sensation
- anxiety, depression, mood changes
- confusion hallucinations
- problems with sexual function
- sleep problems, unusual dreams
- worsening of psoriasis
- hearing disturbances
- tingling or numbness in the hands or feet, cold limbs
- muscle spasms
- excessive sweating
- dry mouth
Tell your doctor immediately or go to casualty at the nearest hospital if you notice any of the following:
- chest tightness, wheezing, shortness of breath
- very slow heart beat
- fast, irregular heart beat, palpitations
- chest pain
- any type of skin rash, itching
- shortness of breath (sometimes with tiredness, weakness and reduced ability to exercise), which may occur together with swelling of the feet or legs due to fluid build up
- fainting
This is not a complete list of all possible side effects. Others may occur in some people and there may be some side effects not yet known.
Tell your doctor if you notice anything that is making you feel unwell while you are taking, or soon after you have finished taking SOTOCOR, even if it is not on this list.
While you are taking it
Things you must do
Tell your doctor if you become pregnant while taking SOTACOR. You doctor can discuss with the risks of taking it while you are pregnant.
If you are about to be started on any new medicine, remind your doctor or pharmacist that you are taking SOTACOR.
Tell any other doctor, dentist, or pharmacist who treats you that you are taking this medicine.
Things you must not do
Do not give your medicine to anyone else, even if they have the same condition as you.
Do not take SOTACOR to treat any other complaints unless your doctor tells you to.
Do not let yourself run out of tablets over weekends or on holidays.
After taking it
Storage
Store your tablets safely in a cool dry place. Protect from light and moisture.
Do not store SOTACOR or any other medicine in the bathroom or near a sink.
Do not leave it in the car on hot days or on window sills. Heat and dampness can destroy some medicines.
Keep your tablets in the original packaging they are provided in until it is time to take them. If you take the tablets out of the blister they will not keep well.
Keep all medicines out of the reach of children. A locked cupboard at least one-and-a-half meters above the ground is a good place to store medicines.
Product description
What it looks like
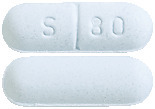
SOTACOR 80mg tablets are light blue, biconvex, capsule shaped tablets, plain on one side and engraved 'S', '80' and a break bar on the other side.
SOTACOR 160mg are light blue biconvex, capsule shaped tablets, plain on one side and engraved 'S', '160' and a break bar on the other side.
Active ingredients
SOTACOR 80mg tablets contain 80mg sotalol hydrochloride per tablets
SOTACOR 160mg tablets contain 160mg sotalol hydrochloride per tablet
The tablets also contain:
- microcrystalline cellulose
- magnesium stearate
- maize starch
- lactose (anhydrous)
- stearic acid
- colloidal anhydrous silica
- indigo carmine (CI 73015)
This medicine contains sugars as lactose.
Sponsor
Arrow Pharma Pty Ltd
15-17 Chapel Street
Cremorne VIC 3121
Australia Registration Numbers:
SOTACOR Tablets 80mg AUST R 68964 in blister pack of 60 tablets
SOTACOR Tablets 160mg AUST R 68966 in blister pack of 60 tablets
This leaflet was revised in December 2022
Published by MIMS February 2023