What is in this leaflet
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine.
This leaflet answers some of the common questions about STRIBILD tablets. It does not contain all of the available information.
It does not take the place of talking to your doctor or pharmacist about your medical condition or treatment. If you have further questions, please ask your doctor or your pharmacist.
Keep this leaflet with your STRIBILD medicine.
You may need to read it again.
This medicine has been prescribed for you personally and you should not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
What is STRIBILD
STRIBILD is used to treat HIV infection. STRIBILD is for people who have never taken HIV medicines before, or who do not have a resistant HIV virus to STRIBILD.
STRIBILD consists of four medicines:
- tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, also called tenofovir DF (VIREAD®)
- emtricitabine or FTC (EMTRIVA®)
- elvitegravir
- cobicistat (TYBOST®)
These are combined in one tablet to help control Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) infection.
VIREAD and EMTRIVA belong to a group of antiviral medicines known as nucleoside and nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTI).
Elvitegravir belongs to a class of antiviral medicines known as integrase inhibitors.
Cobicistat is a “booster”, to help increase the levels of elvitegravir.
How STRIBILD works
HIV infection destroys CD4 T cells, which are important to the immune system. The immune system helps fight infection. After a large number of T cells are destroyed, acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) may develop.
STRIBILD helps block HIV-1 reverse transcriptase, a viral chemical in your body (enzyme) that is needed for HIV-1 to multiply. STRIBILD lowers the amount of HIV in the blood (viral load). STRIBILD may also help to increase the number of T cells (CD4+ cells), allowing your immune system to improve. Lowering the amount of HIV in the blood lowers the chance of death or infections that happen when your immune system is weak (opportunistic infections).
Use in Children and Elderly
STRIBILD is for adults. STRIBILD has not been studied in children under the age of 18 or adults over the age of 65.
Does STRIBILD cure HIV OR AIDS
STRIBILD does not cure HIV infection or AIDS.
The long-term effects of STRIBILD are not known at this time. People taking STRIBILD may still get opportunistic infections or other conditions that happen with HIV infection. Opportunistic infections are infections that develop because the immune system is weakened.
Some of these conditions are:
- pneumonia,
- herpes virus infections, and
- Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) infection.
This medicine is only available from a pharmacist after it has been prescribed by a doctor who specialises in the treatment of HIV infection.
If you wish to continue receiving treatment with STRIBILD it is important you remain under the care of a hospital or doctor who specialises in the treatment of HIV infection.
Does STRIBILD reduce the risk of passing HIV to others
STRIBILD does not lower your chance of passing HIV to other people through sexual contact, sharing needles, or being exposed to your blood.
For your health and the health of others, it is important to always practice safer sex by using a latex or polyurethane condom or other barrier to lower the chance of sexual contact with semen, vaginal secretions, or blood.
Never re-use or share needles.
Before you take STRIBILD
Who must not take it
Together with your doctor, you need to decide whether STRIBILD is right for you.
Do not take STRIBILD if you are allergic to:
- tenofovir
- tenofovir DF
- emtricitabine
- elvitegravir
- cobicistat or
- any of the other ingredients of STRIBILD
Some of the symptoms of an allergic reaction may include:
- shortness of breath
- wheezing or difficulty breathing
- rash, itching or hives on the skin
- swelling of the face, lips, tongue or other parts of the body
The ingredients of STRIBILD are listed in the product description section of this leaflet.
Do not take STRIBILD if you are already taking any other medicines that contain the same active ingredients.
Do not take STRIBILD if you are taking tenofovir alafenamide.
Do not take STRIBILD if you are taking other medicines that contain:
- lamivudine (e.g. Combivir, Zeffix, Kivexa, Trizivir)
- ritonavir (e.g. Kaletra)
- efavirenz (e.g. Stocrin)
Do not take STRIBILD if you are already taking any of the following medicines:
- carbamazepine (e.g. Tegretol)
- phenobarbital
- phenytoin (e.g. Dilantin)
- lovastatin (e.g. Mevacor)
- midazolam (e.g. Hypnovel)
- rifabutin (e.g. Mycobutin)
- rifampicin (e.g. Rifadin/Rimycin)
- sildenafil (e.g. Viagra/Revatio)
- simvastatin (e.g. Invast/Zimcol)
- tadalafil (e.g. Cialis/Adcirca)
- triazolam (e.g. Halcion)
- St John’s Wort or products containing St John’s Wort.
- alfuzosin hydrochloride (e.g. Xatral)
- ergot-containing medicines like dihydroergotamine, ergotamine (e.g. Cafergot, Dihydergot, Migerot).
Do not take STRIBILD to treat your HIV infection if you are also taking adefovir dipivoxil to treat your hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection.
This is not a complete list of medicines that you should tell your doctor about.
Do not take STRIBILD after the expiry or “use by” date (EXP) printed on the bottle. If you take it after the expiry date has passed, it may not work as well.
Do not take STRIBILD if the packaging is torn or shows signs of tampering.
Before you start to take it
Tell your doctor if you take an antacid medicine that contains aluminum, magnesium hydroxide, or calcium carbonate. Take antacids at least 2 hours before or after you take STRIBILD.
Tell your doctor if you are allergic to foods, dyes, preservatives or any other medicines.
Tell your doctor if you are pregnant, or likely to become pregnant during your course of medication. We do not know if STRIBILD can harm your unborn child. You and your doctor will need to decide if STRIBILD is right for you.
Tell your doctor if you are breastfeeding, or likely to breastfeed during your course of medication. You should not breastfeed if you are HIV-positive because of the chance of passing the HIV virus to your baby. Two active substances in this medicine (tenofovir disoproxil fumarate and emtricitabine) have been found in breast milk at low concentrations.
Talk with your doctor about the best way to feed your baby.
Tell your doctor if you have kidney problems or are undergoing kidney dialysis treatment.
Tell your doctor if you have bone problems.
Tell your doctor if you have liver problems, including hepatitis B or C virus infection.
Tell your doctor if you are taking medication to treat your hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection (e.g. ledipasvir/sofosbuvir [HARVONI], sofosbuvir/velpatasvir [EPCLUSA], or sofosbuvir/velpatasvir/ voxilaprevir [VOSEVI]).
Taking other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking any other medicines including any that you buy without a prescription from your pharmacy, supermarket or health food shop.
Some medicines may affect the levels of STRIBILD or STRIBILD may affect the levels of other medicines in the body when they are taken at the same time as STRIBILD.
Your doctor may change your other medicines or change their doses. Other medicines, including herbal products may affect STRIBILD.
For this reason, it is very important to let your doctor or pharmacist know what medications, herbal supplements, or vitamins you are taking.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of medicines and show it to your doctor and pharmacist when you get a new medicine. Your doctor and your pharmacist can tell you if you can take these medicines with STRIBILD.
Do not start any new medicines while you are taking STRIBILD without first talking with your doctor or pharmacist.
How to take STRIBILD
Take the exact amount of STRIBILD your doctor has prescribed for you.
Never change the dose on your own.
Do not stop this medicine unless your healthcare provider tells you to stop.
How much to take
The usual dose is one STRIBILD tablet orally, once daily.
How to take it
Always take STRIBILD with a meal. A meal is important to get the right drug levels in your body.
A protein drink does not constitute a meal.
If you forget to take STRIBILD
Do not miss a dose of STRIBILD.
If you forget to take STRIBILD, take your missed dose right away unless it is almost time for your next dose.
Do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose. Continue with your regular dosing schedule.
When your STRIBILD supply starts to run low, get more from your doctor or pharmacy. This is very important because the amount of virus in your blood may increase if the medicine is stopped for even a short time. The virus may develop resistance to STRIBILD and become harder to treat.
Do not change your dose or stop taking STRIBILD without first talking to your doctor.
If you take too much (overdose)
Immediately telephone your doctor or Poisons Information Centre: 131126 (Australia) and 0800 764 766 (New Zealand) or go to the Accident and Emergency department at your nearest hospital if you think you or anyone else may have taken too many STRIBILD tablets. Do this even if there are no signs of discomfort or poisoning. This may need urgent medical attention.
While you are taking STRIBILD
Things you must not do
Do not breastfeed. See “Before you start to take it”.
Avoid doing things that can spread HIV infection since STRIBILD does not stop you from passing the HIV infection to others:
- Do not share needles or other injection equipment.
- Do not share personal items that can have blood or body fluids on them, like toothbrushes or razor blades.
-
Do not have any kind of sex without protection.
Always practice safer sex by using a latex or polyurethane condom or other barrier to reduce the chance of sexual contact with semen, vaginal secretions, or blood.
Things to be careful of
Be careful driving or operating machinery until you know how STRIBILD affects you. If you are dizzy, have trouble concentrating, or are drowsy, avoid activities that may be dangerous, such as driving or operating machinery.
SIDE EFFECTS
Like all medicines, STRIBILD can have side effects, although not everybody gets them. Some may be serious and need medical attention.
Check with your doctor as soon as possible if you have any problems while taking STRIBILD, even if you do not think the problems are connected with the medicine or are not listed in this leaflet.
STRIBILD may cause the following serious side effects:
Lactic Acidosis
If you have any of the following symptoms after taking your medication, tell your doctor IMMEDIATELY or go to the accident and emergency department at your nearest hospital:
- You feel very weak or tired
- You have unusual (not normal) muscle pain
- You have trouble breathing
- You have stomach pain with nausea and vomiting
- You feel cold, especially in your arms and legs
- You feel dizzy or light headed
- You have a fast or irregular heartbeat
These side effects may be due to a condition called lactic acidosis (build-up of an acid in the blood).
Lactic acidosis can be a medical emergency and may need to be treated in the hospital.
Serious Liver Problems (hepatotoxicity)
If you have any of the following symptoms while taking your medication, tell your doctor IMMEDIATELY or go to the accident and emergency department at your nearest hospital:
- Your skin or the white part of your eyes turns yellow (jaundice)
- Your urine turns dark
- Your bowel movements (stools) turn light in colour
- You don’t feel like eating food for several days or longer
- You feel sick to your stomach (nausea)
- You have lower stomach area (abdominal) pain
These side effects may be due to a condition called hepatotoxicity with liver enlargement (hepatomegaly) and fat deposits in the liver (steatosis) which sometimes occurs in patients taking anti-HIV medicines.
You may be more likely to get lactic acidosis or liver problems if you are female, very overweight (obese), or have been taking similar nucleoside analog-containing medicines, like STRIBILD, for a long time.
Hepatic Flares
If you have HIV infection and HBV infection you should not stop your STRIBILD treatment without first discussing this with your doctor. Some patients have had blood tests or symptoms indicating a worsening of their hepatitis (“hepatic flare”) after stopping individual components (tenofovir DF and emtricitabine) of STRIBILD.
You may require medical exams and blood tests for several months after stopping treatment. STRIBILD is not approved for the treatment of HBV, so you must discuss your HBV therapy with your doctor.
Kidney Problems
If you have had kidney problems in the past or take other medicines that can cause kidney problems, your doctor should do regular blood tests to check your kidneys.
Symptoms that may be related to kidney problems include a high volume of urine, thirst, muscle pain, and muscle weakness.
Changes in Bone Mineral Density (thinning bones)
Laboratory tests show changes in the bones of patients treated with tenofovir DF, a component of STRIBILD.
Some people living with HIV treated with VIREAD developed thinning of the bones (osteopaenia).
If you have had bone problems in the past, your doctor may need to do tests to check your bone mineral density or may prescribe medicines to help your bone mineral density.
Additionally, bone pain and softening of the bone (which may contribute to fractures) may occur as a consequence of kidney problems.
Signs and Symptoms of Inflammation
In some patients with advanced HIV infection (AIDS), signs and symptoms of inflammation from previous infections may occur soon after anti-HIV treatment is started. It is believed that these symptoms are due to an improvement in the body’s immune response, which lets the body fight infections that may have been present with no obvious symptoms.
If you notice any symptoms of infection, please tell your doctor immediately.
Pancreatitis
If you have any of the following symptoms after starting your medication, tell your doctor IMMEDIATELY or go to the accident and emergency department at your nearest hospital:
- severe stomach pain or cramps
- nausea
- vomiting
These side effects may be due to a condition called pancreatitis which sometimes occurs in patients taking anti-HIV medicines.
Common Side Effects:
The most common side effects of STRIBILD are:
- diarrhoea
- upper respiratory tract infection
- depression
Other side effects include:
- vomiting
- nausea
- headache
- intestinal gas
- dizziness
- back pain
- tiredness
- sleeping problems (including difficulty falling asleep or sleepiness)
- bronchitis
- abnormal dreams
- stomach pain or discomfort
- rash
- serious kidney problems
Tell your doctor if you notice anything else that is making you feel unwell.
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist if you don’t understand anything in this list.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist for a more complete list of side effects of STRIBILD and all the medicines you will take. This is not a complete list of side effects possible with STRIBILD.
After taking STRIBILD
Storage
Keep STRIBILD tablets where children cannot reach them. A locked cupboard at least one-and-a half metres above the ground is a good place to store them.
Keep STRIBILD tablets in a cool, dry place where it stays below 30 °C.
Do not store STRIBILD or any other medicine in a bathroom or near a sink.
Do not leave STRIBILD in the car or on a window sill. Heat and dampness can destroy some medicines.
Keep your STRIBILD tablets in the bottle with the cap tightly closed until you take them. If you take STRIBILD tablets out of their pack they may not keep well.
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
What the tablets look like
STRIBILD is the brand name of your medicine.
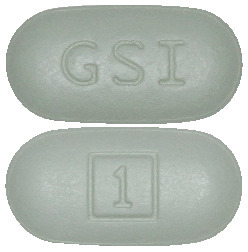
STRIBILD tablets are capsule-shaped and green in colour.
Each tablet is debossed with “GSI” on one side and the number “1” surrounded by a square box ( ) on the other side.
) on the other side.
STRIBILD tablets are supplied in bottles containing 30 tablets.
Ingredients
Each STRIBILD tablet contains the following active ingredients:
- elvitegravir
- cobicistat
- tenofovir disoproxil fumarate
- emtricitabine
Each STRIBILD tablet also contains the following ingredients:
- lactose
- cellulose-microcrystalline (E460)
- silicon dioxide
- croscarmellose sodium
- hyprolose
- magnesium stearate (E572)
- sodium lauryl sulphate
Film-coating:
- indigo carmine (FD&C blue #2)
- aluminum lake
- macrogol 3350
- polyvinyl alcohol
- talc
- titanium dioxide (E171)
- yellow iron oxide
SPONSOR
STRIBILD tablets are supplied in Australia by:
Gilead Sciences Pty Ltd
Level 6, 417 St Kilda Road
Melbourne, Victoria 3004
In New Zealand by:
Gilead Sciences (NZ)
c/- Grant Thornton New Zealand Limited
Level 4, 152 Fanshawe Street,
Auckland 1010
Date of preparation: 15 July 2020
AUST R 194081
ATRIPLA, EPCLUSA, HARVONI, STRIBILD, GENVOYA, DESCOVY, ODEFSEY, EMTRIVA, TRUVADA, EVIPLERA, VIREAD, VOSEVI and GSI are trademarks of Gilead Sciences, Inc. or one of its related companies. All other trademarks referenced herein are the property of their respective owners.
Published by MIMS September 2020