What is in this leaflet
This leaflet answers some common questions about Zithromax. It does not contain all the available information.
It does not take the place of talking to your doctor or pharmacist.
All medicines have risks and benefits. Your doctor has weighed the risks of you taking Zithromax against the benefits they expect it will have for you.
If you have any concerns about taking this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Keep this leaflet with your medicine. You may need to read it again.
What Zithromax is used for
Zithromax is used to treat infections in different parts of the body caused by bacteria.
It is commonly used to treat Chlamydia. Zithromax is also used to prevent infections by a bacterium called Mycobacterium Avium-intracellulare Complex (MAC) in some people.
Zithromax is an antibiotic, which belongs to a group of medicines called azalides.
The azalides are a sub-class of a group of antibiotics called macrolides.
Zithromax works by killing or stopping the growth of bacteria causing your infection.
Zithromax will not work against viral infections such as colds or flu.
Ask your doctor if you have any questions about why Zithromax has been prescribed for you. Your doctor may have prescribed it for another reason.
Zithromax is only available with a doctor's prescription.
This medicine is not addictive.
This medicine is not expected to affect your ability to drive a car or operate machinery.
Before you take Zithromax
When you must not take it
Do not take Zithromax if you are allergic to:
- azithromycin
- any other macrolide or ketolide antibiotics (e.g., clarithromycin, erythromycin, roxithromycin, telithromycin)
- any of the ingredients listed at the end of this leaflet.
Symptoms of an allergic reaction may include shortness of breath, wheezing or difficulty breathing; swelling of the face, lips, tongue or other parts of the body; rash, itching or hives on the skin.
Do not take this medicine if the expiry date (EXP) printed on the packaging has passed or if the packaging is torn or shows signs of tampering. If it has expired or is damaged, return it to your pharmacist for disposal.
If you are not sure whether you should start taking this medicine, talk to your doctor.
Before you start to take it
Tell your doctor if you have allergies to any other medicines, foods, preservatives or dyes.
Tell your doctor if you have any other health problems, including:
- any liver problems
- any kidney problems
- any heart problems, including abnormalities of the rhythm
- diabetes, hereditary fructose intolerance, glucose-galactose malabsorption or saccharise-isomaltase deficiency
- cystic fibrosis
- muscle weakness
- low levels of potassium or magnesium in your blood
- if you are pregnant or if you plan to become pregnant or are breastfeeding. Your doctor can discuss with you the risks and benefits involved.
If you have not told your doctor about any of the above, tell them before you start taking Zithromax.
Taking other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking any other medicines, including any that you get without a prescription from a pharmacy, supermarket or health food shop.
Some medicines may interfere with Zithromax or increase the risk of side effects. These include:
- antacids (medicines used to treat indigestion)
- colchicine (a medicine used to treat gout)
- coumarin-type oral anti-coagulants (a medicine used to prevent blood clots)
- cyclosporin (a medicine used to prevent organ transplant rejection or to treat certain problems with the immune system)
- digoxin (a medicine used to treat abnormal heart rhythm or heart failure)
- ergot derivatives (such as ergotamine, which is used to treat migraines)
- terfenadine or astemizole (medicines used to treat allergies and hay fever)
- zidovudine, a medicine used to treat patients with AIDS
- diphenoxylate (Lomotil), a medicine used to treat diarrhoea
- some medicines used to treat heart rhythm problems (heart arrhythmia) such as amiodarone, disopyramide, ibutilide and sotalol
- antipsychotic medicines used to treat schizophrenia or bipolar mania such as haloperidol, quetiapine and risperidone
- medicines used to treat depression (antidepressants) such as fluoxetine, sertraline and venlafaxine
- fluoroquinolone antibiotics such as ciprofloxacin, lomefloxacin, moxifloxacin and norfloxacin
These medicines may be affected by Zithromax or may affect how well it works. You may need different amounts of your medicines, or you may need to take different medicines.
Your doctor or pharmacist has more information on medicines to be careful with or to avoid while taking Zithromax.
Talk to your doctor about the need for additional contraception while taking Zithromax. Some antibiotics may decrease the effectiveness of some birth control pills, although this has not been shown with Zithromax.
How to take Zithromax
Follow all directions given to you by your doctor or pharmacist carefully. They may differ from the information contained in this leaflet.
If you do not understand the instructions on the pack, ask your doctor or pharmacist for help.
How much to take
The dose will depend on your infection.
The usual dose to treat Chlamydia is two 500 mg tablets taken as a single dose.
For other infections Zithromax is usually taken once a day. Sometimes the dose is taken once a week. Your doctor will decide the right dose for you.
The dose for your child will depend on his or her body weight. Zithromax oral suspension is for use by children.
Your pharmacist will explain how to use it if you are not sure.
How to take it
Tablets:
Swallow the tablets whole with liquid.
Oral Suspension:
Shake the bottle well before use and use the measuring syringe supplied.
Zithromax may be taken with or without food.
If you are taking an antacid (e.g., Gastrogel, Mylanta), take it at least one hour before or two hours after your Zithromax dose. This will avoid any possible effect of the antacid on the absorption of Zithromax.
How long to take it
Continue taking Zithromax until you finish the pack or bottle or until your doctor recommends.
Do not stop taking it because you are feeling better. If you do not complete the full course prescribed by your doctor, the infection may not clear completely or your symptoms may return.
If you are not sure how long you should be taking Zithromax, check with your doctor.
If you forget to take it
If you are taking Zithromax for three days or longer and you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember (within a 24- hour period), then continue as normal.
Do not try to make up for missed doses by taking more than one dose at a time.
If you are not sure what to do, check with your doctor or pharmacist.
If you have trouble remembering to take your Zithromax, ask your pharmacist for some hints.
If you take too much (Overdose)
Immediately telephone your doctor or Poisons Information Centre (13 11 26) for advice if you think that you or anyone else may have taken too much Zithromax. Do this even if there are no signs of discomfort or poisoning. You may need urgent medical attention.
If you take too many tablets or too much oral suspension, you may get an upset stomach, diarrhoea or skin rashes.
While you are using Zithromax
Things you must do
If the symptoms of your infection do not improve within a few days, or if they become worse, tell your doctor.
If you get severe diarrhoea, tell your doctor, pharmacist or nurse immediately. Do this even if it occurs several weeks after Zithromax has been stopped. Diarrhoea may mean that you have a serious condition affecting your bowel. You may need urgent medical care. Do not take any diarrhoea medicine without first checking with your doctor.
If you get a sore, white mouth or tongue while taking, or soon after stopping Zithromax, tell your doctor. Also tell your doctor if you get vaginal itching or discharge. This may mean you have a yeast infection called thrush. Sometimes the use of Zithromax allows yeast to grow and the above symptoms to occur. Zithromax does not work against yeast.
If you become pregnant while taking Zithromax, tell your doctor.
Tell your doctor immediately if during treatment with Zithromax your baby develops irritability with feeding or starts vomiting. This may be a sign of a stomach disorder in the infant.
If you are about to start any new medicines, tell your doctor and pharmacist that you are taking Zithromax.
Tell any other doctors, dentists and pharmacists who are treating you that you are taking Zithromax.
Things you must not do
Do not stop taking Zithromax or lower the dosage without checking with your doctor.
If you do not complete the full course prescribed by your doctor, all the organisms causing your infection may not be killed. These organisms may continue to grow and multiply so that your infection may not clear completely or may return.
Do not give Zithromax to anyone else, even if they have the same condition as you.
Do not use Zithromax to treat any other medical complaints unless your doctor tells you to.
Things to be careful of
Protect your skin when you are in the sun, especially between 10am and 3pm. Some macrolide antibiotics may cause your skin to be more sensitive to sunlight than it is normally. Exposure to sunlight may cause a skin rash, itching, redness or severe sunburn.
If outdoors, wear protective clothing and use a 30+ sunscreen. If your skin does appear to be burning tell your doctor immediately.
Side effects
Tell your doctor or pharmacist as soon as possible if you do not feel well while you are taking Zithromax.
Like other medicines, Zithromax can cause some side effects. If they occur, most are likely to be minor and temporary. However, some may be serious and need medical attention.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist to answer any questions you may have.
Do not be alarmed by the following list of side effects. You may not experience any of them.
While taking it
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you notice any of the following and they worry you:
- oral thrush - white, furry, sore tongue and mouth
- vaginal thrush - sore and itchy vagina and/or white discharge
- nausea (feeling sick), loss of appetite, vomiting, stomach pain, indigestion, wind, constipation, diarrhoea
- dizziness, headache, spinning sensation
- tiredness, drowsiness, fatigue
- muscle or joint aches
- rash
- hearing loss or ringing in the ears
- altered taste and smell.
These side effects are usually mild.
See your doctor immediately and before you take your next dose of Zithromax if you notice any of the following:
- severe persistent diarrhoea (loose bowel motions)
- fast or irregular heart beat
- symptoms of sunburn such as redness, itching, swelling or blistering which may occur more quickly than normal
- decreased feeling or sensitivity, especially in the skin
- hives, itching or skin rash
- widespread body rash, fever and swollen lymph nodes
- aggressive reaction, nervousness, agitation or anxiety
- bleeding or bruising more easily than normal, reddish or purplish blotches under the skin
- signs of frequent or worrying infections such as fever, severe chills, sore throat or mouth ulcers
- dark urine or blood in the urine or bowel motions
- severe upper stomach pain, often with nausea and vomiting.
These are serious side effects. You may need urgent medical attention. Serious side effects are rare.
If any of the following happen, stop taking Zithromax and tell your doctor immediately or go to casualty at your nearest hospital:
- sudden signs of allergy such as rash, itching or hives on the skin, swelling of the face, lips, tongue or other parts of the body, shortness of breath, wheezing or trouble breathing
- blisters or ulcers on the skin, in the mouth or airways that may occur after a period of fever
- diarrhoea, usually with blood and mucus, stomach pain and fever
- yellowing of the eyes or skin, also called jaundice
- chest pain
- fainting
- convulsions (fits)
These are very serious side effects. You may need urgent medical attention or hospitalisation. These side effects are rare.
After finishing it
Tell your doctor immediately if you notice any of the following side effects, particularly if they occur several weeks after stopping treatment with Zithromax:
- severe stomach cramps
- watery and severe diarrhoea, which may be bloody
- fever, in combination with one or both of the above.
Zithromax can cause some bacteria, which are normally present in the bowel and normally harmless to multiply and therefore cause the above symptoms. You may need urgent medical attention. However this side effect is rare.
Do not take any medicine for this diarrhoea without first checking with your doctor.
Tell your doctor if you notice anything else that is making you feel unwell. Other side effects not listed above may also occur in some patients. Some of these side effects (for example certain liver conditions, and blood abnormalities) can only be found when your doctor does tests from time to time to check your progress.
Do not be alarmed at this list of possible side effects. You may not experience any of them
After using Zithromax
Storage
Keep Zithromax in its original packaging until it is time to use it.
If you take Zithromax out of its packaging, it may not keep as well.
Keep your Zithromax in a cool, dry place where the temperature stays below 30°C.
Do not store Zithromax or any other medicine in the bathroom or near a sink. Do not leave it in the car or on a window sill. Heat and dampness can destroy some medicines.
Keep your Zithromax where young children cannot reach it. A locked cupboard at least one-and-a-half metres above the ground is a good place to store medicines.
Disposal
If your doctor tells you to stop taking this medicine, or it has passed its expiry date, ask your pharmacist what to do with any that is left over.
Discard any oral suspension left over after 10 days.
Product description
What it looks like
Zithromax tablets come in two strengths:
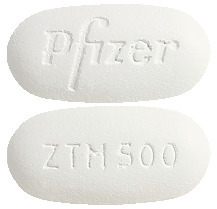
- Zithromax 500 mg - white to off white, unscored, modified capsule-shaped film coated tablets, engraved with 'ZTM 500' on one side and 'Pfizer' on the other. Blister packs of 2 and 3.
- Zithromax 600 mg - white to off white, scored, modified oval film coated tablets, engraved with 'ZTM 600' on one side and 'PFIZER' on the other. Blister pack of 8.
- Zithromax Powder for Oral Suspension is a white to off-white powder in a 15 mL bottle, and it is an off-white to orange to brown liquid when made up with water.
Ingredients
Active ingredient
500 mg Tablets
- 500 mg azithromycin per tablet
600 mg Tablets
- 600 mg azithromycin per tablet
Powder for Oral Suspension
- 200 mg azithromycin per 5 mL
Other ingredients
Tablets
- pregelatinsed-maize starch
- calcium hydrogen phosphate
- croscarmellose sodium
- magnesium stearate
- sodium lauryl sulfate
- lactose
- hypromellose
- titanium dioxide
- glycerol triacetin
Powder for Oral Suspension
- sucrose
- sodium phosphate
- hyprolose
- xanthan gum
- cherry flavour
- banana flavour
- vanilla flavour (contains milk products)
Supplier
Pfizer Australia Pty Ltd
Sydney NSW
Toll Free Number: 1800 675 229
Australian Registration Numbers
500 mg Tablets: AUST R 58797
600 mg Tablets: AUST R 60057
Powder for Oral Suspension
200 mg/5mL: AUST R 60049
This leaflet was prepared in January 2022.
© Pfizer Australia Pty Ltd 2022
® Registered Trademark
Published by MIMS March 2022